Integrin inhibition promotes atypical anoikis in glioma cells
- PMID: 24457956
- PMCID: PMC4040659
- DOI: 10.1038/cddis.2013.543
Integrin inhibition promotes atypical anoikis in glioma cells
Abstract
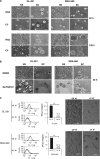
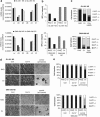
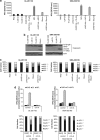
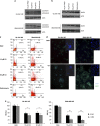
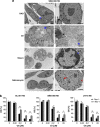
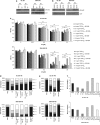
Integrins regulate cellular adhesion and transmit signals important for cell survival, proliferation and motility. They are expressed by glioma cells and may contribute to their malignant phenotype. Integrin inhibition may therefore represent a promising therapeutic strategy. GL-261 and SMA-560 glioma cells grown under standard conditions uniformly detached and formed large cell clusters after integrin gene silencing or pharmacological inhibition using EMD-121974, a synthetic Arg-Gly-Asp-motif peptide, or GLPG0187, a nonpeptidic integrin inhibitor. After 120 h, the clusters induced by integrin inhibition decayed and cells died. In contrast, when cells were cultured under stem cell (sphere) conditions, no disaggregation became apparent upon integrin inhibition, and cell death was not observed. As poly-HEMA-mediated detachment had similar effects on cell viability as integrin inhibition, we postulated that cell death may result from detachment alone, which was confirmed using various permissive and nonpermissive substrates. No surrogate markers of apoptosis were detected and electron microscopy confirmed that necrosis represents the dominant morphology of detachment-induced cell death. In addition, integrin inhibition resulted in the induction of autophagy that represents a survival signal. When integrins were inhibited in nonsphere glioma cells, the TGF-β pathway was strongly impaired, whereas no such effect was observed in glioma cells cultured under sphere conditions. Cell death induced by integrin inhibition was rescued by the addition of recombinant transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β) and accelerated by exposure to the TGF-β receptor inhibitor, SD-208. In summary, cell death following integrin inhibition is detachment mediated, represents an atypical form of anoikis involving necrosis as well as autophagy, and is modulated by TGF-β pathway activity.
Figures


References
-
- Mitra SK, Schlaepfer DD. Integrin-regulated FAK-Src signaling in normal and cancer cells. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2006;18:516–523. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

