Regulation of the proapoptotic functions of prostate apoptosis response-4 (Par-4) by casein kinase 2 in prostate cancer cells
- PMID: 24457960
- PMCID: PMC4040712
- DOI: 10.1038/cddis.2013.532
Regulation of the proapoptotic functions of prostate apoptosis response-4 (Par-4) by casein kinase 2 in prostate cancer cells
Abstract
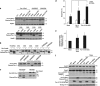
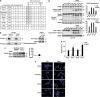
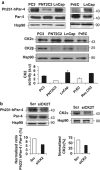
The proapoptotic protein, prostate apoptosis response-4 (Par-4), acts as a tumor suppressor in prostate cancer cells. The serine/threonine kinase casein kinase 2 (CK2) has a well-reported role in prostate cancer resistance to apoptotic agents or anticancer drugs. However, the mechanistic understanding on how CK2 supports survival is far from complete. In this work, we demonstrate both in rat and humans that (i) Par-4 is a new substrate of the survival kinase CK2 and (ii) phosphorylation by CK2 impairs Par-4 proapoptotic functions. We also unravel different levels of CK2-dependent regulation of Par-4 between species. In rats, the phosphorylation by CK2 at the major site, S124, prevents caspase-mediated Par-4 cleavage (D123) and consequently impairs the proapoptotic function of Par-4. In humans, CK2 strongly impairs the apoptotic properties of Par-4, independently of the caspase-mediated cleavage of Par-4 (D131), by triggering the phosphorylation at residue S231. Furthermore, we show that human Par-4 residue S231 is highly phosphorylated in prostate cancer cells as compared with their normal counterparts. Finally, the sensitivity of prostate cancer cells to apoptosis by CK2 knockdown is significantly reversed by parallel knockdown of Par-4. Thus, Par-4 seems a critical target of CK2 that could be exploited for the development of new anticancer drugs.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Role of protein kinase CK2 in the regulation of tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis inducing ligand-induced apoptosis in prostate cancer cells.Cancer Res. 2006 Feb 15;66(4):2242-9. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-2772. Cancer Res. 2006. PMID: 16489027
-
Influence of casein kinase II in tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand-induced apoptosis in human rhabdomyosarcoma cells.Clin Cancer Res. 2004 Oct 1;10(19):6650-60. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-04-0576. Clin Cancer Res. 2004. PMID: 15475455
-
Intracellular hydrogen peroxide production is an upstream event in apoptosis induced by down-regulation of casein kinase 2 in prostate cancer cells.Mol Cancer Res. 2006 May;4(5):331-8. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-06-0073. Mol Cancer Res. 2006. PMID: 16687488
-
CK2 signaling in androgen-dependent and -independent prostate cancer.J Cell Biochem. 2006 Oct 1;99(2):382-91. doi: 10.1002/jcb.20847. J Cell Biochem. 2006. PMID: 16598768 Review.
-
[Casein kinase 2, the versatile regulator of cell survival].Mol Biol (Mosk). 2012 May-Jun;46(3):423-33. Mol Biol (Mosk). 2012. PMID: 22888632 Review. Russian.
Cited by
-
Structural Analysis of the cl-Par-4 Tumor Suppressor as a Function of Ionic Environment.Biomolecules. 2021 Mar 5;11(3):386. doi: 10.3390/biom11030386. Biomolecules. 2021. PMID: 33807852 Free PMC article.
-
A Naturally Generated Decoy of the Prostate Apoptosis Response-4 Protein Overcomes Therapy Resistance in Tumors.Cancer Res. 2017 Aug 1;77(15):4039-4050. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-16-1970. Epub 2017 Jun 16. Cancer Res. 2017. PMID: 28625975 Free PMC article.
-
Prostate apoptosis response-4 and tumor suppression: it's not just about apoptosis anymore.Cell Death Dis. 2021 Jan 7;12(1):47. doi: 10.1038/s41419-020-03292-1. Cell Death Dis. 2021. PMID: 33414404 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Par-4 overexpression impedes leukemogenesis in the Eµ-TCL1 leukemia model through downregulation of NF-κB signaling.Blood Adv. 2019 Apr 23;3(8):1255-1266. doi: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2018025973. Blood Adv. 2019. PMID: 30987970 Free PMC article.
-
CK2α' Drives Lung Cancer Metastasis by Targeting BRMS1 Nuclear Export and Degradation.Cancer Res. 2016 May 1;76(9):2675-86. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-15-2888. Epub 2016 Mar 15. Cancer Res. 2016. PMID: 26980766 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chakraborty M, Qiu SG, Vasudevan KM, Rangnekar VM. Par-4 drives trafficking and activation of Fas and Fasl to induce prostate cancer cell apoptosis and tumor regression. Cancer Res. 2001;61:7255–7263. - PubMed
-
- El-Guendy N, Rangnekar VM. Apoptosis by Par-4 in cancer and neurodegenerative diseases. Exp Cell Res. 2003;283:51–66. - PubMed
-
- Nalca A, Qiu SG, El-Guendy N, Krishnan S, Rangnekar VM. Oncogenic Ras sensitizes cells to apoptosis by Par-4. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:29976–29983. - PubMed
-
- Sells StephenF, Wood DP, Joshi-barve SS, Muthukumar S, Jacob RJ, Crist SA, et al. Commonality of apoptosis of the gene programs in androgen-dependent prostate cells. Cell Growth Differs. 1994;5:457–466. - PubMed
-
- Mattson MP, Duan W, Chan SL, Camandola S. Par-4: an emerging pivotal player in neuronal apoptosis and neurodegenerative disorders. J Mol Neurosci. 1999;13:17–30. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

