A cell-penetrating peptide based on the interaction between c-Src and connexin43 reverses glioma stem cell phenotype
- PMID: 24457967
- PMCID: PMC4040690
- DOI: 10.1038/cddis.2013.560
A cell-penetrating peptide based on the interaction between c-Src and connexin43 reverses glioma stem cell phenotype
Abstract
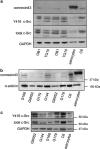
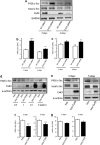
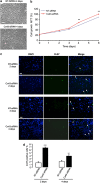
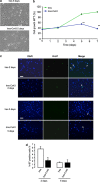
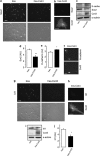
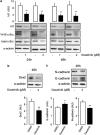
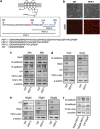
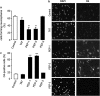
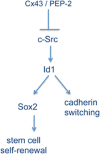
Connexin43 (Cx43), the main gap junction channel-forming protein in astrocytes, is downregulated in malignant gliomas. These tumors are composed of a heterogeneous population of cells that include many with stem-cell-like properties, called glioma stem cells (GSCs), which are highly tumorigenic and lack Cx43 expression. Interestingly, restoring Cx43 reverses GSC phenotype and consequently reduces their tumorigenicity. In this study, we investigated the mechanism by which Cx43 exerts its antitumorigenic effects on GSCs. We have focused on the tyrosine kinase c-Src, which interacts with the intracellular carboxy tail of Cx43. We found that Cx43 regulates c-Src activity and proliferation in human GSCs expanded in adherent culture. Thus, restoring Cx43 in GSCs inhibited c-Src activity, which in turn promoted the downregulation of the inhibitor of differentiation Id1. Id1 sustains stem cell phenotype as it controls the expression of Sox2, responsible for stem cell self-renewal, and promotes cadherin switching, which has been associated to epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Our results show that both the ectopic expression of Cx43 and the inhibition of c-Src reduced Id1, Sox2 expression and promoted the switch from N- to E-cadherin, suggesting that Cx43, by inhibiting c-Src, downregulates Id1 with the subsequent changes in stem cell phenotype. On the basis of this mechanism, we found that a cell-penetrating peptide, containing the region of Cx43 that interacts with c-Src, mimics the effect of Cx43 on GSC phenotype, confirming the relevance of the interaction between Cx43 and c-Src in the regulation of the malignant phenotype and pinpointing this interaction as a promising therapeutic target.
Figures
References
-
- Giaume C, Koulakoff A, Roux L, Holcman D, Rouach N. Astroglial networks: a step further in neuroglial and gliovascular interactions. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2010;11:87–99. - PubMed
-
- Rouach N, Koulakoff A, Abudara V, Willecke K, Giaume C. Astroglial metabolic networks sustain hippocampal synaptic transmission. Science. 2008;322:1551–1555. - PubMed
-
- Loewenstein WR, Kanno Y. Intercellular communication and the control of tissue growth: lack of communication between cancer cells. Nature. 1966;209:1248–1249. - PubMed
-
- Naus CC, Laird DW. Implications and challenges of connexin connections to cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2010;10:435–441. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

