Calcium channel α2δ1 proteins mediate trigeminal neuropathic pain states associated with aberrant excitatory synaptogenesis
- PMID: 24459143
- PMCID: PMC3945363
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M114.548990
Calcium channel α2δ1 proteins mediate trigeminal neuropathic pain states associated with aberrant excitatory synaptogenesis
Abstract
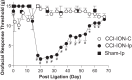
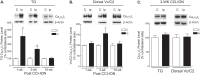
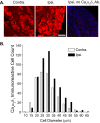
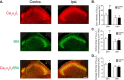
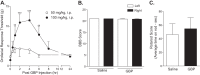
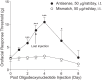
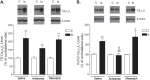
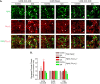
To investigate a potential mechanism underlying trigeminal nerve injury-induced orofacial hypersensitivity, we used a rat model of chronic constriction injury to the infraorbital nerve (CCI-ION) to study whether CCI-ION caused calcium channel α2δ1 (Cavα2δ1) protein dysregulation in trigeminal ganglia and associated spinal subnucleus caudalis and C1/C2 cervical dorsal spinal cord (Vc/C2). Furthermore, we studied whether this neuroplasticity contributed to spinal neuron sensitization and neuropathic pain states. CCI-ION caused orofacial hypersensitivity that correlated with Cavα2δ1 up-regulation in trigeminal ganglion neurons and Vc/C2. Blocking Cavα2δ1 with gabapentin, a ligand for the Cavα2δ1 proteins, or Cavα2δ1 antisense oligodeoxynucleotides led to a reversal of orofacial hypersensitivity, supporting an important role of Cavα2δ1 in orofacial pain processing. Importantly, increased Cavα2δ1 in Vc/C2 superficial dorsal horn was associated with increased excitatory synaptogenesis and increased frequency, but not the amplitude, of miniature excitatory postsynaptic currents in dorsal horn neurons that could be blocked by gabapentin. Thus, CCI-ION-induced Cavα2δ1 up-regulation may contribute to orofacial neuropathic pain states through abnormal excitatory synapse formation and enhanced presynaptic excitatory neurotransmitter release in Vc/C2.
Keywords: Gene Regulation; Molecular Pharmacology; Neuroscience; Pain; Synaptic Plasticity.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Synaptic ultrastructure changes in trigeminocervical complex posttrigeminal nerve injury.J Comp Neurol. 2016 Feb 1;524(2):309-22. doi: 10.1002/cne.23844. Epub 2015 Jul 16. J Comp Neurol. 2016. PMID: 26132987 Free PMC article.
-
Trigeminal nerve injury-induced thrombospondin-4 up-regulation contributes to orofacial neuropathic pain states in a rat model.Eur J Pain. 2014 Apr;18(4):489-95. doi: 10.1002/j.1532-2149.2013.00396.x. Epub 2013 Sep 9. Eur J Pain. 2014. PMID: 24019258 Free PMC article.
-
Calcium Channel α2δ1 Subunit Mediates Secondary Orofacial Hyperalgesia Through PKC-TRPA1/Gap Junction Signaling.J Pain. 2020 Jan-Feb;21(1-2):238-257. doi: 10.1016/j.jpain.2019.08.012. Epub 2019 Sep 5. J Pain. 2020. PMID: 31494272
-
Non-neuronal cells act as crucial players in neuropathic orofacial pain.J Oral Biosci. 2024 Sep;66(3):491-495. doi: 10.1016/j.job.2024.07.005. Epub 2024 Jul 18. J Oral Biosci. 2024. PMID: 39032826 Review.
-
Neuron-glia interaction is a key mechanism underlying persistent orofacial pain.J Oral Sci. 2017;59(2):173-175. doi: 10.2334/josnusd.16-0858. J Oral Sci. 2017. PMID: 28637974 Review.
Cited by
-
The EGF-LIKE domain of thrombospondin-4 is a key determinant in the development of pain states due to increased excitatory synaptogenesis.J Biol Chem. 2018 Oct 19;293(42):16453-16463. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA118.003591. Epub 2018 Sep 7. J Biol Chem. 2018. PMID: 30194282 Free PMC article.
-
Mirogabalin for the management of postherpetic neuralgia: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 3 study in Asian patients.Pain. 2019 May;160(5):1175-1185. doi: 10.1097/j.pain.0000000000001501. Pain. 2019. PMID: 30913164 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Direct, gabapentin-insensitive interaction of a soluble form of the calcium channel subunit α2δ-1 with thrombospondin-4.Sci Rep. 2019 Nov 7;9(1):16272. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-52655-y. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31700036 Free PMC article.
-
Potential Molecular Targets for Treating Neuropathic Orofacial Pain Based on Current Findings in Animal Models.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jun 15;22(12):6406. doi: 10.3390/ijms22126406. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34203854 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Calcium Signalling in Breast Cancer Associated Bone Pain.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Feb 8;23(3):1902. doi: 10.3390/ijms23031902. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35163823 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hardt J., Jacobsen C., Goldberg J., Nickel R., Buchwald D. (2008) Prevalence of chronic pain in a representative sample in the United States. Pain Med. 9, 803–812 - PubMed
-
- Clark G. T. (2006) Persistent orodental pain, atypical odontalgia, and phantom tooth pain: when are they neuropathic disorders? J. Calif. Dent. Assoc. 34, 599–609 - PubMed
-
- Vickers E. R., Cousins M. J. (2000) Neuropathic orofacial pain. Part 2—diagnostic procedures, treatment guidelines and case reports. Aust. Endod. J. 26, 53–63 - PubMed
-
- Gee N. S., Brown J. P., Dissanayake V. U., Offord J., Thurlow R., Woodruff G. N. (1996) The novel anticonvulsant drug, gabapentin (Neurontin), binds to the α2δ subunit of a calcium channel. J. Biol. Chem. 271, 5768–5776 - PubMed
-
- Marais E., Klugbauer N., Hofmann F. (2001) Calcium channel α2δ subunits—structure and gabapentin binding. Mol. Pharmacol. 59, 1243–1248 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

