Effect of mitral inflow pattern on diagnosis of severe mitral regurgitation in patients with chronic organic mitral regurgitation
- PMID: 24459563
- PMCID: PMC3894367
- DOI: 10.4250/jcu.2013.21.4.165
Effect of mitral inflow pattern on diagnosis of severe mitral regurgitation in patients with chronic organic mitral regurgitation
Abstract
Background: To determine sensitivity and specificity of E wave velocity in patients with severe chronic organic mitral regurgitation (MR) and normal left ventricular ejection fraction (EF) and to evaluate prevalence of A wave dominance in patients with severe MR.
Methods: We compared 35 patients with quantified severe, chronic, quantified, organic MR due to flail/prolapsed leaflets who had reparative surgery with 35 age-matched control subjects.
Exclusion criteria: EF < 60%, atrial fibrillation, and more than mild aortic regurgitation.
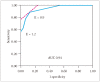
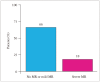
Results: Mean [standard deviation (SD)] age [70 (8) years vs. 69 (8) years; p = 0.94] and mean (SD) EF [66% (6%) vs. 65% (4%); p = 0.43] were not different between the two groups. Mean (SD) E wave velocity was greater in case patients than control subjects [1.2 (0.3) m/sec vs. 0.7 (0.15) m/sec; p < 0.001]. However, E wave velocity of 1.2 m/sec had a sensitivity of only 57% [95% confidence interval (CI), 41-7 and a specificity of 100% (95% CI, 90-100%) in identifying severe MR. E wave velocity of 0.9 m/sec had a more optimal combined sensitivity (89%; 95% CI, 74-95%) and specificity (86%; 95% CI, 71-94%). A wave dominance was seen in 18% of case patients and 66% of control subjects (p < 0.001).
Conclusion: E wave velocity of 1.2 m/sec is specific not sensitive for severe organic MR; E wave velocity of 0.9 m/sec has better sensitivity and specificity. A wave dominance pattern alone cannot exclude patients with severe organic MR. Our findings highlight the importance of a comprehensive echocardiographic exam rather than relying on a few Doppler parameters in diagnosing MR.
Keywords: A wave velocity; Diastolic function; E wave velocity; Severe mitral regurgitation.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Usefulness of peak mitral inflow velocity to predict severe mitral regurgitation in patients with normal or impaired left ventricular systolic function.Am Heart J. 2001 Dec;142(6):1065-71. doi: 10.1067/mhj.2001.118465. Am Heart J. 2001. PMID: 11717613 Clinical Trial.
-
Characteristic Doppler echocardiographic pattern of mitral inflow velocity in severe aortic regurgitation.J Am Coll Cardiol. 1989 Dec;14(7):1712-7. doi: 10.1016/0735-1097(89)90021-1. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1989. PMID: 2584560
-
Prognostic impact of peak mitral inflow velocity in asymptomatic degenerative mitral regurgitation.Heart. 2019 Apr;105(8):609-615. doi: 10.1136/heartjnl-2018-313733. Epub 2018 Oct 20. Heart. 2019. PMID: 30343285
-
Peak mitral inflow velocity predicts mitral regurgitation severity.J Am Coll Cardiol. 1998 Jan;31(1):174-9. doi: 10.1016/s0735-1097(97)00454-3. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1998. PMID: 9426037
-
Noninvasive assessment of left ventricular relaxation using continuous-wave Doppler aortic regurgitant velocity curve. Its comparative value to the mitral regurgitation method.Circulation. 1995 Jan 1;91(1):192-200. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.91.1.192. Circulation. 1995. PMID: 7805202
Cited by
-
The role of E-wave velocity in predicting early left ventricular dysfunction and significant decline in left ventricular ejection fraction after mitral valve repair for severe chronic primary mitral regurgitation.Heart Vessels. 2025 Apr;40(4):320-331. doi: 10.1007/s00380-024-02468-5. Epub 2024 Oct 8. Heart Vessels. 2025. PMID: 39375196
References
-
- Enriquez-Sarano M, Avierinos JF, Messika-Zeitoun D, Detaint D, Capps M, Nkomo V, Scott C, Schaff HV, Tajik AJ. Quantitative determinants of the outcome of asymptomatic mitral regurgitation. N Engl J Med. 2005;352:875–883. - PubMed
-
- Thomas L, Foster E, Schiller NB. Peak mitral inflow velocity predicts mitral regurgitation severity. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1998;31:174–179. - PubMed
-
- Zoghbi WA, Enriquez-Sarano M, Foster E, Grayburn PA, Kraft CD, Levine RA, Nihoyannopoulos P, Otto CM, Quinones MA, Rakowski H, Stewart WJ, Waggoner A, Weissman NJ American Society of Echocardiography. Recommendations for evaluation of the severity of native valvular regurgitation with two-dimensional and Doppler echocardiography. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2003;16:777–802. - PubMed
-
- Lancellotti P, Moura L, Pierard LA, Agricola E, Popescu BA, Tribouilloy C, Hagendorff A, Monin JL, Badano L, Zamorano JL European Association of Echocardiography. European Association of Echocardiography recommendations for the assessment of valvular regurgitation. Part 2: mitral and tricuspid regurgitation (native valve disease) Eur J Echocardiogr. 2010;11:307–332. - PubMed
-
- Recusani F, Bargiggia GS, Yoganathan AP, Raisaro A, Valdes-Cruz LM, Sung HW, Bertucci C, Gallati M, Moises VA, Simpson IA. A new method for quantification of regurgitant flow rate using color Doppler flow imaging of the flow convergence region proximal to a discrete orifice. An in vitro study. Circulation. 1991;83:594–604. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

