Pre-Clinical Evaluation of rHDL Encapsulated Retinoids for the Treatment of Neuroblastoma
- PMID: 24459664
- PMCID: PMC3891009
- DOI: 10.3389/fped.2013.00006
Pre-Clinical Evaluation of rHDL Encapsulated Retinoids for the Treatment of Neuroblastoma
Abstract
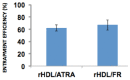
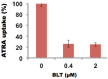
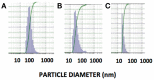
Despite major advances in pediatric cancer research, there has been only modest progress in the survival of children with high risk neuroblastoma (NB) (HRNB). The long term survival rates of HRNB in the United States are still only 30-50%. Due to resistance that often develops during therapy, development of new effective strategies is essential to improve the survival and overcome the tendency of HRNB patients to relapse subsequent to initial treatment. Current chemotherapy regimens also have a serious limitation due to off target toxicity. In the present work, we evaluated the potential application of reconstituted high density lipoprotein (rHDL) containing fenretinide (FR) nanoparticles as a novel approach to current NB therapeutics. The characterization and stability studies of rHDL-FR nanoparticles showed small size (<40 nm) and high encapsulation efficiency. The cytotoxicity studies of free FR vs. rHDL/FR toward the NB cell lines SK-N-SH and SMS-KCNR showed 2.8- and 2-fold lower IC50 values for the rHDL encapsulated FR vs. free FR. More importantly, the IC50 value for retinal pigment epithelial cells (ARPE-19), a recipient of off target toxicity during FR therapy, was over 40 times higher for the rHDL/FR as compared to that of free FR. The overall improvement in in vitro selective therapeutic efficiency was thus about 100-fold upon encapsulation of the drug into the rHDL nanoparticles. These studies support the potential value of this novel drug delivery platform for treating pediatric cancers in general, and NB in particular.
Keywords: all-trans-retinoic acid; drug delivery; fenretinide; nanoparticles; neuroblastoma; rHDL.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Reconstituted high density lipoprotein mediated targeted co-delivery of HZ08 and paclitaxel enhances the efficacy of paclitaxel in multidrug-resistant MCF-7 breast cancer cells.Eur J Pharm Sci. 2016 Sep 20;92:11-21. doi: 10.1016/j.ejps.2016.06.017. Epub 2016 Jun 23. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2016. PMID: 27343697
-
Enhanced solubility and functionality of valrubicin (AD-32) against cancer cells upon encapsulation into biocompatible nanoparticles.Int J Nanomedicine. 2012;7:975-83. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S28029. Epub 2012 Feb 22. Int J Nanomedicine. 2012. PMID: 22393294 Free PMC article.
-
Retinoic-acid-resistant neuroblastoma cell lines show altered MYC regulation and high sensitivity to fenretinide.Med Pediatr Oncol. 2000 Dec;35(6):597-602. doi: 10.1002/1096-911x(20001201)35:6<597::aid-mpo23>3.0.co;2-b. Med Pediatr Oncol. 2000. PMID: 11107126
-
Evaluation of reconstituted high-density lipoprotein (rHDL) as a drug delivery platform - a detailed survey of rHDL particles ranging from biophysical properties to clinical implications.Nanomedicine. 2016 Oct;12(7):2161-2179. doi: 10.1016/j.nano.2016.05.009. Epub 2016 May 26. Nanomedicine. 2016. PMID: 27237620 Review.
-
Reconstituted HDL: Drug Delivery Platform for Overcoming Biological Barriers to Cancer Therapy.Front Pharmacol. 2018 Oct 15;9:1154. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2018.01154. eCollection 2018. Front Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 30374303 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Superparamagnetic reconstituted high-density lipoprotein nanocarriers for magnetically guided drug delivery.Int J Nanomedicine. 2017 Feb 22;12:1453-1464. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S122036. eCollection 2017. Int J Nanomedicine. 2017. PMID: 28260891 Free PMC article.
-
Synthetic high-density lipoprotein-like nanoparticles for cancer therapy.Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 2015 Jan;15(1):27-34. doi: 10.1586/14737140.2015.990889. Epub 2014 Dec 9. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 2015. PMID: 25487833 Free PMC article. Review.
-
High-Density Lipoproteins for Therapeutic Delivery Systems.J Mater Chem B. 2016 Jan 14;4(2):188-197. doi: 10.1039/C5TB01332A. Epub 2015 Nov 24. J Mater Chem B. 2016. PMID: 27069624 Free PMC article.
-
Results of a phase I-II study of fenretinide and rituximab for patients with indolent B-cell lymphoma and mantle cell lymphoma.Br J Haematol. 2017 Feb;176(4):583-590. doi: 10.1111/bjh.14451. Epub 2017 Jan 5. Br J Haematol. 2017. PMID: 28055107 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
SR-B1-targeted nanodelivery of anti-cancer agents: a promising new approach to treat triple-negative breast cancer.Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press). 2017 Jun 2;9:383-392. doi: 10.2147/BCTT.S131038. eCollection 2017. Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press). 2017. PMID: 28670138 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

