Role of a histamine 4 receptor as an anti-inflammatory target in carrageenan-induced pleurisy in mice
- PMID: 24460575
- PMCID: PMC4080953
- DOI: 10.1111/imm.12257
Role of a histamine 4 receptor as an anti-inflammatory target in carrageenan-induced pleurisy in mice
Abstract
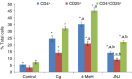
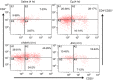
The histamine 4 receptor (H4R) is expressed primarily on cells involved in inflammation and immune responses. Despite much research into inflammatory diseases, no drugs with favourable safety profiles are yet available for their treatment. The aim of the present study was to determine the potential anti-inflammatory effect of 4-methylhistamine (4-MeH) or JNJ77777120 (JNJ) and to explore the role of H4R in a mouse model of carrageenan (Cg) -induced pleurisy. A single dose of 4-MeH or JNJ (30 mg/kg) was administered intraperitoneally 1 hr before Cg administration. The results illustrate that both the numbers of CD4(+) , CD25(+) , CD4(+) CD25(+) , GITR(+) , GITR(+) IL-17A(+) -expressing T cells and the levels of T helper type 1 (Th1)/Th17 cytokines were markedly increased in both the Cg-treated and 4-MeH-treated groups, whereas the cytokines produced by Th2 cells were significantly decreased in the same groups. However, JNJ treatment significantly decreased both the number of T-cell subsets and GITR(+) , GITR(+) IL-17A(+) -expressing T cells, and the production of Th1/Th17 cytokines. Further, JNJ up-regulated the expression of the Th2 cytokines. RT-PCR analysis revealed an increased expression of interleukin-1β, tumour necrosis factor-α, monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 and intercellular adhesion molecule-1 in the Cg-treated and 4-MeH-treated groups, which was reduced by treatment with JNJ in lung tissues. Moreover, histological examinations revealed anti-inflammatory effects of JNJ, whereas 4-MeH worsened Cg-induced inflammation. In conclusion, the results of the present work clearly indicate that JNJ possesses important anti-inflammatory properties that are increased in 4-MeH-treated mice, suggesting that H4R are involved in pleurisy and that JNJ has an anti-inflammatory effect in associated disease conditions.
Keywords: 4-methylhistamine dihydrochloride; GITR-expressing cells; JNJ77777120; cytokines; histamine 4 receptor; λ-Carrageenan-induced inflammation.
© 2014 John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Histamine 4 receptor promotes expression of costimulatory B7.1/B7.2 molecules, CD28 signaling and cytokine production in stress-induced immune responses.J Neuroimmunol. 2015 Dec 15;289:30-42. doi: 10.1016/j.jneuroim.2015.10.008. Epub 2015 Oct 22. J Neuroimmunol. 2015. PMID: 26616869
-
Involvement of histamine 4 receptor in the pathogenesis and progression of rheumatoid arthritis.Int Immunol. 2014 Jun;26(6):325-40. doi: 10.1093/intimm/dxt075. Epub 2014 Jan 8. Int Immunol. 2014. PMID: 24402309
-
Regulation of TNF-α and NF-κB activation through the JAK/STAT signaling pathway downstream of histamine 4 receptor in a rat model of LPS-induced joint inflammation.Immunobiology. 2015 Jul;220(7):889-98. doi: 10.1016/j.imbio.2015.01.008. Epub 2015 Jan 30. Immunobiology. 2015. PMID: 25666529
-
Stimulation of the histamine 4 receptor with 4-methylhistamine modulates the effects of chronic stress on the Th1/Th2 cytokine balance.Immunobiology. 2015 Mar;220(3):341-9. doi: 10.1016/j.imbio.2014.10.014. Epub 2014 Oct 24. Immunobiology. 2015. PMID: 25457414
-
Clinical Development of Histamine H4 Receptor Antagonists.Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2017;241:301-320. doi: 10.1007/164_2016_130. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2017. PMID: 28233185 Review.
Cited by
-
Analgesic and Anti-Arthritic Potential of Methanolic Extract and Palmatine Obtained from Annona squamosa Leaves.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024 Oct 5;17(10):1331. doi: 10.3390/ph17101331. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39458972 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacological targeting of allergen-specific T lymphocytes.Immunol Lett. 2017 Sep;189:27-39. doi: 10.1016/j.imlet.2017.03.010. Epub 2017 Mar 18. Immunol Lett. 2017. PMID: 28322861 Free PMC article. Review.
-
P-FN12, an H4R-Based Epitope Vaccine Screened by Phage Display, Regulates the Th1/Th2 Balance in Rat Allergic Rhinitis.Mol Ther Methods Clin Dev. 2018 Oct 4;11:83-91. doi: 10.1016/j.omtm.2018.09.004. eCollection 2018 Dec 14. Mol Ther Methods Clin Dev. 2018. PMID: 30417023 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Modeling of Histamine Receptors-Recent Advances in Drug Discovery.Molecules. 2021 Mar 22;26(6):1778. doi: 10.3390/molecules26061778. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 33810008 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Histamine H4 Receptor Agonist, 4-Methylhistamine, Aggravates Disease Progression and Promotes Pro-Inflammatory Signaling in B Cells in an Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis Mouse Model.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Aug 20;24(16):12991. doi: 10.3390/ijms241612991. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37629172 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Passani MB, Giannoni P, Bucherelli C, Baldi E, Blandina P. Histamine in the brain: beyond sleep and memory. Biochem Pharmacol. 2007;73:1113–22. - PubMed
-
- Schneider E, Rolli-Derkinderen M, Arock M, Dy M. Trends in histamine research: new functions during immune responses and hematopoiesis. Trends Immunol. 2002;23:255–63. - PubMed
-
- Haas HL, Sergeeva OA, Selbach O. Histamine in the nervous system. Physiol Rev. 2008;88:1183–241. - PubMed
-
- Liu C, Wilson SJ, Kuei C, Lovenberg TW. Comparison of human, mouse, rat, and guinea pig histamine H4 receptors reveals substantial pharmacological species variation. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2001;299:121–30. - PubMed
-
- De Esch IJ, Thurmond RL, Jongejan A, Leurs R. The histamine H4 receptor as a new therapeutic target for inflammation. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2005;26:462–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

