Pericellular oxygen monitoring with integrated sensor chips for reproducible cell culture experiments
- PMID: 24460744
- PMCID: PMC6496616
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2184.2013.12089.x
Pericellular oxygen monitoring with integrated sensor chips for reproducible cell culture experiments
Abstract
Objectives: Here we present an application, in two tumour cell lines, based on the Sensing Cell Culture Flask system as a cell culture monitoring tool for pericellular oxygen sensing.
Materials and methods: T-47D (human breast cancer) and T98G (human brain cancer) cells were cultured either in atmospheric air or in a glove-box set at 4% oxygen, in both cases with 5% CO2 in the gas phase. Pericellular oxygen tension was measured with the help of an integrated sensor chip comprising oxygen sensor arrays.
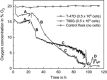
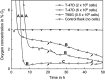
Results: Obtained results illustrate variation of pericellular oxygen tension in attached cells covered by stagnant medium. Independent of incubation conditions, low pericellular oxygen concentration levels, usually associated with hypoxia, were found in dense cell cultures.
Conclusions: Respiration alone brought pericellular oxygen concentration down to levels which could activate hypoxia-sensing regulatory processes in cultures believed to be aerobic. Cells in culture believed to experience conditions of mild hypoxia may, in reality, experience severe hypoxia. This would lead to incorrect assumptions and suggests that pericellular oxygen concentration readings are of great importance to obtain reproducible results when dealing with hypoxic and normoxic (aerobic) incubation conditions. The Sensing Cell Culture Flask system allows continuous monitoring of pericellular oxygen concentration with outstanding long-term stability and no need for recalibration during cell culture experiments. The sensor is integrated into the flask bottom, thus in direct contact with attached cells. No additional equipment needs to be inserted into the flask during culturing. Transparency of the electrochemical sensor chip allows optical inspection of cells attached on top of the sensor.
© 2014 John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures





References
-
- Ebbesen P, Pettersen EO, Gorr TA, Jobst G, Williams K, Kieninger J et al (2009) Taking advantage of tumor cell adaptations to hypoxia for developing new tumor markers and treatment strategies. J. Enzyme Inhib. Med. Chem. 24, 1–39. - PubMed
-
- Ebbesen P, Eckardt K‐U, Ciampor F, Pettersen EO (2004) Linking measured intercellular oxygen concentration to human cell functions. Acta Oncol. 43, 598–600. - PubMed
-
- Boag JW (1970) Cell respiration as a function of oxygen tension. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 18, 475–478. - PubMed
-
- Chapman JD, Sturrock J, Boag JW, Crookall JO (1970) Factors affecting the oxygen tension around cells growing in plastic Petri dishes. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 17, 305–328. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

