A comparison of three techniques (local anesthetic deposited circumferential to vs. above vs. below the nerve) for ultrasound guided femoral nerve block
- PMID: 24460975
- PMCID: PMC3933203
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2253-14-6
A comparison of three techniques (local anesthetic deposited circumferential to vs. above vs. below the nerve) for ultrasound guided femoral nerve block
Abstract
Background: Fractured neck of femur generally requires operative fixation and is a common cause of admission to hospital. The combination of femoral nerve block and spinal anesthesia is a common anesthetic technique used to facilitate the surgical procedure. The optimal disposition of local anesthetic (LA) relative the femoral nerve (FN) has not been defined. Our hypothesis was: that the deposition of LA relative to the FN influences the quality of analgesia for positioning of the patient for performance of spinal anesthesia. The primary outcome was verbal rating (VRS) pain scores 0-10 assessed immediately after positioning the patient to perform spinal anesthesia.
Methods: With Institutional ethical approval and having obtained written informed consent from each, 52 patients were studied. The study was registered with ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT01527812). Patients were randomly allocated to undergo to one of three groups namely: intention to deposit lidocaine 2% (15 ml) i. above (Group A), ii. below (Group B), iii. circumferential (Group C) to the FN. A blinded observer assessed i. the sensory nerve block (cold) in the areas of the terminal branches of the FN and ii. VRS pain scores on passive movement from block completion at 5 minutes intervals for 30 minutes. Immediately after positioning the patient for spinal anesthesia, VRS pain scores were recorded.
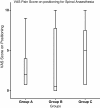
Results: Pain VRS scores during positioning were similar in the three groups [Above group/Below group/Circumferential group: 2(0-9)/0(0-10)/3(0-10), median(range), p:0.32]. The block was deemed to have failed in 20%, 47% and 12% in the Above group, Below group and Circumferential group respectively. The median number of needle passes was greater in the Circumferential group compared with the Above group (p:0.009). Patient satisfaction was greatest in the Circumferential group [mean satisfaction scores were 83.5(19.8)/88.1(20.5)/93.8(12.3), [mean(SD), p=0.04] in the Above, Below and Circumferential groups respectively.
Conclusions: We conclude that there is no clinical advantage to attempting to deposit LA circumferential to the femoral nerve (relative to depositing LA either above or below the nerve), during femoral nerve block in this setting.
Figures



Similar articles
-
The Lateral Femoral Cutaneous Nerve: Description of the Sensory Territory and a Novel Ultrasound-Guided Nerve Block Technique.Reg Anesth Pain Med. 2018 May;43(4):357-366. doi: 10.1097/AAP.0000000000000737. Reg Anesth Pain Med. 2018. PMID: 29381568 Clinical Trial.
-
Ultrasound-guided continuous femoral nerve block: a randomized trial on the influence of femoral nerve catheter orifice configuration (six-hole versus end-hole) on post-operative analgesia after total knee arthroplasty.BMC Anesthesiol. 2018 Dec 19;18(1):191. doi: 10.1186/s12871-018-0648-8. BMC Anesthesiol. 2018. PMID: 30567487 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
A comparison of ultrasound alone vs ultrasound with nerve stimulation guidance for continuous femoral nerve block in patients undergoing total knee arthroplasty.J Clin Anesth. 2016 Aug;32:274-80. doi: 10.1016/j.jclinane.2015.08.012. Epub 2015 Oct 1. J Clin Anesth. 2016. PMID: 26427307 Clinical Trial.
-
The Use of Ultrasound Guidance for Perioperative Neuraxial and Peripheral Nerve Blocks in Children: A Cochrane Review.Anesth Analg. 2017 Mar;124(3):948-958. doi: 10.1213/ANE.0000000000001363. Anesth Analg. 2017. PMID: 27308952 Review.
-
Ultrasound-Guided Nerve Block Anesthesia.Vet Clin North Am Food Anim Pract. 2016 Mar;32(1):133-47. doi: 10.1016/j.cvfa.2015.09.003. Vet Clin North Am Food Anim Pract. 2016. PMID: 26922116 Review.
Cited by
-
An update around the evidence base for the lower extremity ultrasound regional block technique.F1000Res. 2016 Jan 26;5:F1000 Faculty Rev-104. doi: 10.12688/f1000research.7199.1. eCollection 2016. F1000Res. 2016. PMID: 26918177 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Is accepted practice in regional anaesthesia really 'best practice'?BJA Educ. 2022 Mar;22(3):84-86. doi: 10.1016/j.bjae.2021.12.002. Epub 2022 Feb 2. BJA Educ. 2022. PMID: 35211324 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Elliot JM. Regional anaesthesia in trauma. Trauma. 2001;3(3):161–174.
-
- Haddad FS, Williams RL. Femoral nerve block in extracapsular femoral neck fractures. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1995;77-B:922–923. - PubMed
-
- Bernstein RL, Rosenberg AD. Manual of Orthopedic Anaesthesia and Related Pain Syndromes. New York: Churchill Livingstone; 1993.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

