Neuronal matrix metalloproteinase-9 is a determinant of selective neurodegeneration
- PMID: 24462097
- PMCID: PMC6015650
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2013.12.009
Neuronal matrix metalloproteinase-9 is a determinant of selective neurodegeneration
Abstract
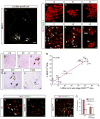
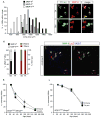
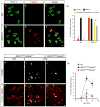
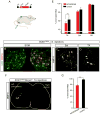
Selective neuronal loss is the hallmark of neurodegenerative diseases. In patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), most motor neurons die but those innervating extraocular, pelvic sphincter, and slow limb muscles exhibit selective resistance. We identified 18 genes that show >10-fold differential expression between resistant and vulnerable motor neurons. One of these, matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9), is expressed only by fast motor neurons, which are selectively vulnerable. In ALS model mice expressing mutant superoxide dismutase (SOD1), reduction of MMP-9 function using gene ablation, viral gene therapy, or pharmacological inhibition significantly delayed muscle denervation. In the presence of mutant SOD1, MMP-9 expressed by fast motor neurons themselves enhances activation of ER stress and is sufficient to trigger axonal die-back. These findings define MMP-9 as a candidate therapeutic target for ALS. The molecular basis of neuronal diversity thus provides significant insights into mechanisms of selective vulnerability to neurodegeneration.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures



Comment in
-
Neurodegenerative disease: Searching for the weak spots.Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2014 Apr;13(4):256. doi: 10.1038/nrd4284. Epub 2014 Mar 21. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2014. PMID: 24658311 No abstract available.
References
-
- Alexianu ME, Ho BK, Mohamed AH, La Bella V, Smith RG, Appel SH. The role of calcium-binding proteins in selective motoneuron vulnerability in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Ann Neurol. 1994;36:846–858. - PubMed
-
- Aronica E, Catania MV, Geurts J, Yankaya B, Troost D. Immunohistochemical localization of group I and II metabotropic glutamate receptors in control and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis human spinal cord: upregulation in reactive astrocytes. Neuroscience. 2001;105:509–520. - PubMed
-
- Brockington A, Ning K, Heath PR, Wood E, Kirby J, Fusi N, Lawrence N, Wharton SB, Ince PG, Shaw PJ. Unravelling the enigma of selective vulnerability in neurodegeneration: motor neurons resistant to degeneration in ALS show distinct gene expression characteristics and decreased susceptibility to excitotoxicity. Acta Neuropathol. 2013;125:95–109. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cleveland DW, Rothstein JD. From Charcot to Lou Gehrig: deciphering selective motor neuron death in ALS. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2001;2:806–819. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

