Ultrasound-mediated blood-brain barrier disruption for targeted drug delivery in the central nervous system
- PMID: 24462453
- PMCID: PMC4041837
- DOI: 10.1016/j.addr.2014.01.008
Ultrasound-mediated blood-brain barrier disruption for targeted drug delivery in the central nervous system
Abstract
The physiology of the vasculature in the central nervous system (CNS), which includes the blood-brain barrier (BBB) and other factors, complicates the delivery of most drugs to the brain. Different methods have been used to bypass the BBB, but they have limitations such as being invasive, non-targeted or requiring the formulation of new drugs. Focused ultrasound (FUS), when combined with circulating microbubbles, is a noninvasive method to locally and transiently disrupt the BBB at discrete targets. This review provides insight on the current status of this unique drug delivery technique, experience in preclinical models, and potential for clinical translation. If translated to humans, this method would offer a flexible means to target therapeutics to desired points or volumes in the brain, and enable the whole arsenal of drugs in the CNS that are currently prevented by the BBB.
Keywords: Brain; Drug delivery; Microbubbles; Ultrasound.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
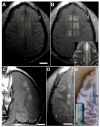
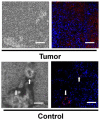
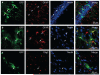
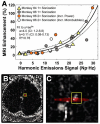
Figures





References
-
- Neuwelt EA, Bauer B, Fahlke C, Fricker G, Iadecola C, Janigro D, Leybaert L, Molnar Z, O'Donnell ME, Povlishock JT, Saunders NR, Sharp F, Stanimirovic D, Watts RJ, Drewes LR. Engaging neuroscience to advance translational research in brain barrier biology. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2011;12:169–182. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Abbott NJ, Romero IA. Transporting therapeutics across the blood-brain barrier. Mol. Med Today. 1996;2:106–113. - PubMed
-
- Pardridge WM. Molecular biology of the blood-brain barrier. Mol. Biotechnol. 2005;30:57–70. - PubMed
-
- Minniti G, Amelio D, Amichetti M, Salvati M, Muni R, Bozzao A, Lanzetta G, Scarpino S, Arcella A, Enrici RM. Patterns of failure and comparison of different target volume delineations in patients with glioblastoma treated with conformal radiotherapy plus concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide. Radiother. Oncol. 2010;97:377–381. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

