12-step facilitation for the dually diagnosed: a randomized clinical trial
- PMID: 24462479
- PMCID: PMC3976999
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jsat.2013.12.009
12-step facilitation for the dually diagnosed: a randomized clinical trial
Abstract
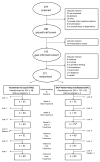
There are few clinical trials of 12-step treatments for individuals with serious mental illness and alcohol or drug dependence. This randomized trial assessed the effects of adding a 12-session 12-step facilitation therapy (TSF), adapted from that used in Project MATCH, to treatment as usual in an outpatient dual diagnosis program. Participants were 121 individuals dually diagnosed with alcohol dependence and a serious mental disorder, followed during 12 weeks of treatment and 36 weeks post-treatment. Participants receiving TSF had greater participation in 12-step programs, but did not demonstrate greater improvement in alcohol and drug use. However, considered dimensionally, greater participation in TSF was associated with greater improvement in substance use, and greater 12-step participation predicted decreases in frequency and intensity of drinking. Findings suggest that future work with TSF in this population should focus on maximizing exposure to TSF, and maximizing the effect of TSF on 12-step participation.
Keywords: 12-step; Alcohol dependence; Alcoholics Anonymous; Clinical trial; Double trouble in recovery; Dual diagnosis; Serious mental illness.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Baigent M, Holme G, Hafner RJ. Self reports of the interaction between substance abuse and schizophrenia. Aust N Z J Psychiatry. 1995;29(1):69–74. - PubMed
-
- Bogenschutz MP, Akin SJ. 12-Step participation and attitudes toward 12-step meetings in dual diagnosis patients. Alcoholism Treatment Quarterly. 2000;18(4):31–45.
-
- Bogenschutz MP, Geppert CM, George J. The role of twelve-step approaches in dual diagnosis treatment and recovery. Am J Addict. 2006;15(1):50–60. - PubMed
-
- Brady JP. Social skills training for psychiatric patients. I: Concepts, methods, and clinical results. Am J Psychiatry. 1984;141(3):333–340. - PubMed
-
- Brooks AJ, Penn PE. Comparing treatments for dual diagnosis: twelve-step and self-management and recovery training. Am J Drug Alcohol Abuse. 2003;29(2):359–383. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical