Cloud-based bioinformatics workflow platform for large-scale next-generation sequencing analyses
- PMID: 24462600
- PMCID: PMC4203338
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jbi.2014.01.005
Cloud-based bioinformatics workflow platform for large-scale next-generation sequencing analyses
Abstract
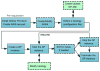
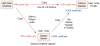
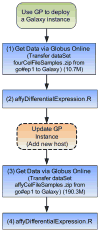
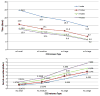
Due to the upcoming data deluge of genome data, the need for storing and processing large-scale genome data, easy access to biomedical analyses tools, efficient data sharing and retrieval has presented significant challenges. The variability in data volume results in variable computing and storage requirements, therefore biomedical researchers are pursuing more reliable, dynamic and convenient methods for conducting sequencing analyses. This paper proposes a Cloud-based bioinformatics workflow platform for large-scale next-generation sequencing analyses, which enables reliable and highly scalable execution of sequencing analyses workflows in a fully automated manner. Our platform extends the existing Galaxy workflow system by adding data management capabilities for transferring large quantities of data efficiently and reliably (via Globus Transfer), domain-specific analyses tools preconfigured for immediate use by researchers (via user-specific tools integration), automatic deployment on Cloud for on-demand resource allocation and pay-as-you-go pricing (via Globus Provision), a Cloud provisioning tool for auto-scaling (via HTCondor scheduler), and the support for validating the correctness of workflows (via semantic verification tools). Two bioinformatics workflow use cases as well as performance evaluation are presented to validate the feasibility of the proposed approach.
Keywords: Bioinformatics; Cloud computing; Galaxy; Scientific workflow; Sequencing analyses.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures







References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

