Dapagliflozin improves muscle insulin sensitivity but enhances endogenous glucose production
- PMID: 24463448
- PMCID: PMC3904617
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI70704
Dapagliflozin improves muscle insulin sensitivity but enhances endogenous glucose production
Erratum in
- J Clin Invest. 2014 May 1;124(5):2287
Abstract
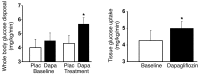
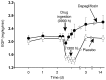
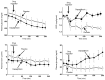
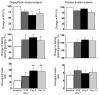
Chronic hyperglycemia impairs insulin action, resulting in glucotoxicity, which can be ameliorated in animal models by inducing glucosuria with renal glucose transport inhibitors. Here, we examined whether reduction of plasma glucose with a sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitor could improve insulin-mediated tissue glucose disposal in patients with type 2 diabetes. Eighteen diabetic men were randomized to receive either dapagliflozin (n = 12) or placebo (n = 6) for 2 weeks. We measured insulin-mediated whole body glucose uptake and endogenous glucose production (EGP) at baseline and 2 weeks after treatment using the euglycemic hyperinsulinemic clamp technique. Dapagliflozin treatment induced glucosuria and markedly lowered fasting plasma glucose. Insulin-mediated tissue glucose disposal increased by approximately 18% after 2 weeks of dapagliflozin treatment, while placebo-treated subjects had no change in insulin sensitivity. Surprisingly, following dapagliflozin treatment, EGP increased substantially and was accompanied by an increase in fasting plasma glucagon concentration. Together, our data indicate that reduction of plasma glucose with an agent that works specifically on the kidney to induce glucosuria improves muscle insulin sensitivity. However, glucosuria induction following SGLT2 inhibition is associated with a paradoxical increase in EGP. These results provide support for the glucotoxicity hypothesis, which suggests that chronic hyperglycemia impairs insulin action in individuals with type 2 diabetes.
Figures
Comment in
-
Paradoxical insights into whole body metabolic adaptations following SGLT2 inhibition.J Clin Invest. 2014 Feb;124(2):485-7. doi: 10.1172/JCI74297. Epub 2014 Jan 27. J Clin Invest. 2014. PMID: 24463446 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

