Robotic compared with laparoscopic sacrocolpopexy: a randomized controlled trial
- PMID: 24463657
- PMCID: PMC4266590
- DOI: 10.1097/AOG.0000000000000006
Robotic compared with laparoscopic sacrocolpopexy: a randomized controlled trial
Erratum in
- Obstet Gynecol. 2014 Jul;124(1):165
Abstract
Objective: Laparoscopic and robotic sacrocolpopexy are widely used for pelvic organ prolapse (POP) treatment. Evidence comparing outcomes and costs is lacking. We compared costs and clinically relevant outcomes in women randomized to laparoscopic sacrocolpopexy compared with robotic sacrocolpopexy.
Methods: Participants with symptomatic stage POP II or greater, including significant apical support loss, were randomized to either laparoscopic or robotic sacrocolpopexy. We compared surgical costs (including costs for robot, initial hospitalization) and rehospitalization within 6 weeks. Secondary outcomes included postoperative pain, POP quantification, symptom severity and quality of life, and adverse events.
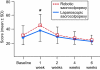
Results: We randomized 78 women (mean age 59 years): laparoscopic (n=38) and robotic (n=40). The robotic sacrocolpopexy group had higher initial hospital costs ($19,616 compared with $11,573, P<.001) and over 6 weeks, hospital costs remained higher for robotic sacrocolpopexy ($20,898 compared with $12,170, P<.001). When we excluded costs of robot purchase and maintenance, we did not detect a statistical difference in initial day of surgery costs of robotic compared with laparoscopic ($12,586 compared with $11,573; P=.160) or hospital costs over 6 weeks ($13,867 compared with $12,170; P=.060). The robotic group had longer operating room times (202.8 minutes compared with 178.4 minutes, P=.030) and higher pain scores 1 week after surgery (3.5±2.1 compared with 2.6±2.2; P=.044). There were no group differences in symptom bother by Pelvic Floor Distress Inventory, POP stage, or rate of adverse events.
Conclusion: Costs of robotic sacrocolpopexy are higher than laparoscopic, whereas short-term outcomes and complications are similar. Primary cost differences resulted from robot maintenance and purchase costs.
Clinical trial registration: Clinicaltrials.gov, www.clinicaltrials.gov, NCT01124916.
Level of evidence: I.
Figures

Comment in
-
Robotics in gynecology: is the glass half empty or half full?Obstet Gynecol. 2014 Jan;123(1):3-4. doi: 10.1097/AOG.0000000000000073. Obstet Gynecol. 2014. PMID: 24463656 No abstract available.
-
Robotic compared with laparoscopic sacrocolpopexy: a randomized controlled trial.Obstet Gynecol. 2014 Jun;123(6):1357-1358. doi: 10.1097/AOG.0000000000000311. Obstet Gynecol. 2014. PMID: 24848908 No abstract available.
References
-
- Geller EJ, Siddiqui NY, Wu JM, Visco AG. Short-term outcomes of robotic sacrocolpopexy compared with abdominal sacrocolpopexy. Obstet Gynecol. 2008;112(6):1201–6. - PubMed
-
- McDermott CD, Hale DS. Abdominal, laparoscopic, and robotic surgery for pelvic organ prolapse. Obstet Gynecol Clin North Am. 2009;36(3):585–614. - PubMed
-
- Pollard ME, Eilber KS, Anger JT. Abdominal approaches to pelvic prolapse repairs. Curr Opin Urol. 2013;23(4):306–11. - PubMed
-
- Patel M, O'Sullivan D, Tulikangas PK. A comparison of costs for abdominal, laparoscopic, and robot-assisted sacral colpopexy. Int Urogynecol J Pelvic Floor Dysfunct. 2009;20(2):223–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

