A review of telehealth service implementation frameworks
- PMID: 24464237
- PMCID: PMC3945538
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph110201279
A review of telehealth service implementation frameworks
Abstract
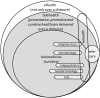
Despite the potential of telehealth services to increase the quality and accessibility of healthcare, the success rate of such services has been disappointing. The purpose of this paper is to find and compare existing frameworks for the implementation of telehealth services that can contribute to the success rate of future endeavors. After a thorough discussion of these frameworks, this paper outlines the development methodologies in terms of theoretical background, methodology and validation. Finally, the common themes and formats are identified for consideration in future implementation. It was confirmed that a holistic implementation approach is needed, which includes technology, organizational structures, change management, economic feasibility, societal impacts, perceptions, user-friendliness, evaluation and evidence, legislation, policy and governance. Furthermore, there is some scope for scientifically rigorous framework development and validation approaches.
Figures
References
-
- South African Government eHealth Strategy for South Africa, 2012–2016. [(accessed on 17 February 2013)]. Available online: http://www.doh.gov.za/docs/stratdocs/2012.
-
- Handler T.J. Hype cycle for telemedicine. Gart. Ind. Res. 2007;G00233474:1–56.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical