Connective tissue growth factor (CCN2) and microRNA-21 are components of a positive feedback loop in pancreatic stellate cells (PSC) during chronic pancreatitis and are exported in PSC-derived exosomes
- PMID: 24464300
- PMCID: PMC4063995
- DOI: 10.1007/s12079-014-0220-3
Connective tissue growth factor (CCN2) and microRNA-21 are components of a positive feedback loop in pancreatic stellate cells (PSC) during chronic pancreatitis and are exported in PSC-derived exosomes
Abstract
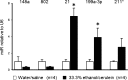
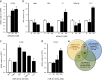
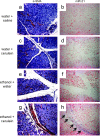
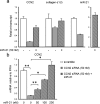
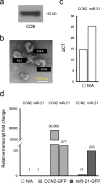
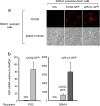
Pancreatitis is an inflammatory condition of the pancreas which, in its chronic form, involves tissue destruction, exocrine and endocrine insufficiency, increased risk of pancreatic cancer, and an extensive fibrotic pathology which is due to unrelenting collagen deposition by pancreatic stellate cells (PSC). In response to noxious agents such as alcohol-excessive consumption of which is a major cause of pancreatitis in the West-normally quiescent PSC undergo a phenotypic and functional transition to activated myofibroblasts which produce and deposit collagen at high levels. This process is regulated by connective tissue growth factor (CCN2), expression of which is highly up-regulated in activated PSC. We show that CCN2 production by activated PSC is associated with enhanced expression of microRNA-21 (miR-21) which was detected at high levels in activated PSC in a murine model of alcoholic chronic pancreatitis. A positive feedback loop between CCN2 and miR-21 was identified that resulted in enhancement of their respective expression as well as that of collagen α1(I). Both miR-21 and CCN2 mRNA were present in PSC-derived exosomes, which were characterized as 50-150 nm CD9-positive nano-vesicles. Exosomes from CCN2-GFP- or miR-21-GFP-transfected PSC were taken up by other PSC cultures, as shown by direct fluorescence or qRT-PCR for GFP. Collectively these studies establish miR-21 and CCN2 as participants in a positive feedback loop during PSC activation and as components of the molecular payload in PSC-derived exosomes that can be delivered to other PSC. Thus interactions between cellular or exosomal miR-21 and CCN2 represent novel aspects of fibrogenic regulation in PSC. Summary Chronic injury in the pancreas is associated with fibrotic pathology which is driven in large part by CCN2-dependent collagen production in pancreatic stellate cells. This study shows that CCN2 up-regulation in PSC is associated with increased expression of miR-21 which, in turn, is able to stimulate CCN2 expression further via a positive feedback loop. Additionally miR-21 and CCN2 were identified in PSC-derived exosomes which effected their delivery to other PSC. The cellular and exosomal miR-21-CCN2 axis is a novel component in PSC fibrogenic signaling.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Fibrogenic Signaling Is Suppressed in Hepatic Stellate Cells through Targeting of Connective Tissue Growth Factor (CCN2) by Cellular or Exosomal MicroRNA-199a-5p.Am J Pathol. 2016 Nov;186(11):2921-2933. doi: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2016.07.011. Epub 2016 Sep 21. Am J Pathol. 2016. PMID: 27662798 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic regulation of connective tissue growth factor by MicroRNA-214 delivery in exosomes from mouse or human hepatic stellate cells.Hepatology. 2014 Mar;59(3):1118-29. doi: 10.1002/hep.26768. Epub 2014 Jan 27. Hepatology. 2014. PMID: 24122827 Free PMC article.
-
Suppression of fibrogenic signaling in hepatic stellate cells by Twist1-dependent microRNA-214 expression: Role of exosomes in horizontal transfer of Twist1.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2015 Sep 15;309(6):G491-9. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00140.2015. Epub 2015 Jul 30. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2015. PMID: 26229009 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of pancreatic function by connective tissue growth factor (CTGF, CCN2).Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2013 Feb;24(1):59-68. doi: 10.1016/j.cytogfr.2012.07.001. Epub 2012 Aug 10. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2013. PMID: 22884427 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Battle-scarred pancreas: role of alcohol and pancreatic stellate cells in pancreatic fibrosis.J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2006 Oct;21 Suppl 3:S97-S101. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1746.2006.04587.x. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2006. PMID: 16958684 Review.
Cited by
-
CCN Proteins (Cellular Communication Network Factors): Expanding Their Repertoire Toward a New Concept.Methods Mol Biol. 2023;2582:1-10. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-2744-0_1. Methods Mol Biol. 2023. PMID: 36370338
-
miRNA and Gene Expression in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma.Am J Pathol. 2019 Jan;189(1):58-70. doi: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2018.10.005. Am J Pathol. 2019. PMID: 30558723 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Resveratrol Inhibits ROS-Promoted Activation and Glycolysis of Pancreatic Stellate Cells via Suppression of miR-21.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2018 Apr 26;2018:1346958. doi: 10.1155/2018/1346958. eCollection 2018. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2018. PMID: 29854071 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase: A Link Between Inflammation and Pancreatic Cancer.Pancreas. 2016 Jan;45(1):21-31. doi: 10.1097/MPA.0000000000000531. Pancreas. 2016. PMID: 26658038 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of exosomes in pancreatic cancer.Oncol Lett. 2021 Apr;21(4):298. doi: 10.3892/ol.2021.12559. Epub 2021 Feb 17. Oncol Lett. 2021. PMID: 33732374 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

