Molecular determinants mediating gating of Transient Receptor Potential Canonical (TRPC) channels by stromal interaction molecule 1 (STIM1)
- PMID: 24464579
- PMCID: PMC3945304
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M113.546556
Molecular determinants mediating gating of Transient Receptor Potential Canonical (TRPC) channels by stromal interaction molecule 1 (STIM1)
Abstract
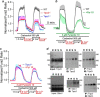
Transient receptor potential canonical (TRPC) channels mediate a critical part of the receptor-evoked Ca(2+) influx. TRPCs are gated open by the endoplasmic reticulum Ca(2+) sensor STIM1. Here we asked which stromal interaction molecule 1 (STIM1) and TRPC domains mediate the interaction between them and how this interaction is used to open the channels. We report that the STIM1 Orai1-activating region domain of STIM1 interacts with the TRPC channel coiled coil domains (CCDs) and that this interaction is essential for opening the channels by STIM1. Thus, disruption of the N-terminal (NT) CCDs by triple mutations eliminated TRPC surface localization and reduced binding of STIM1 to TRPC1 and TRPC5 while increasing binding to TRPC3 and TRPC6. Single mutations in TRPC1 NT or C-terminal (CT) CCDs reduced interaction and activation of TRPC1 by STIM1. Remarkably, single mutations in the TRPC3 NT CCD enhanced interaction and regulation by STIM1. Disruption in the TRPC3 CT CCD eliminated regulation by STIM1 and the enhanced interaction caused by NT CCD mutations. The NT CCD mutations converted TRPC3 from a TRPC1-dependent to a TRPC1-independent, STIM1-regulated channel. TRPC1 reduced the FRET between BFP-TRPC3 and TRPC3-YFP and between CFP-TRPC3-YFP upon stimulation. Accordingly, knockdown of TRPC1 made TRPC3 STIM1-independent. STIM1 dependence of TRPC3 was reconstituted by the TRPC1 CT CCD alone. Knockout of Trpc1 and Trpc3 similarly inhibited Ca(2+) influx, and inhibition of Trpc3 had no further effect on Ca(2+) influx in Trpc1(-/-) cells. Cell stimulation enhanced the formation of Trpc1-Stim1-Trpc3 complexes. These findings support a model in which the TRPC3 NT and CT CCDs interact to shield the CT CCD from interaction with STIM1. The TRPC1 CT CCD dissociates this interaction to allow the STIM1 Orai1-activating region within STIM1 access to the TRPC3 CT CCD and regulation of TRPC3 by STIM1. These studies provide evidence that the TRPC channel CCDs participate in channel gating.
Keywords: Calcium; Calcium Signaling; Gating; Gating Mechanism; STIM1; Signaling; TRP Channels.
Figures
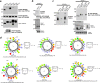
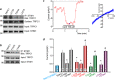
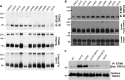
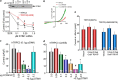


References
-
- Feske S., Gwack Y., Prakriya M., Srikanth S., Puppel S. H., Tanasa B., Hogan P. G., Lewis R. S., Daly M., Rao A. (2006) A mutation in Orai1 causes immune deficiency by abrogating CRAC channel function. Nature 441, 179–185 - PubMed
-
- Birnbaumer L. (2009) The TRPC class of ion channels. A critical review of their roles in slow, sustained increases in intracellular Ca2+ concentrations. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 49, 395–426 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

