CCN2 suppresses catabolic effects of interleukin-1β through α5β1 and αVβ3 integrins in nucleus pulposus cells: implications in intervertebral disc degeneration
- PMID: 24464580
- PMCID: PMC3953253
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M113.526111
CCN2 suppresses catabolic effects of interleukin-1β through α5β1 and αVβ3 integrins in nucleus pulposus cells: implications in intervertebral disc degeneration
Abstract
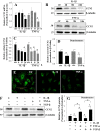
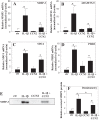
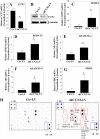
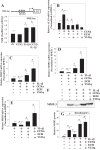
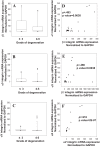
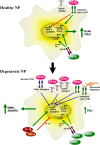
The objective of the study was to examine the regulation of CCN2 by inflammatory cytokines, IL-1β, and TNF-α and to determine whether CCN2 modulates IL-1β-dependent catabolic gene expression in nucleus pulposus (NP) cells. IL-1β and TNF-α suppress CCN2 mRNA and protein expression in an NF-κB-dependent but MAPK-independent manner. The conserved κB sites located at -93/-86 and -546/-537 bp in the CCN2 promoter mediated this suppression. On the other hand, treatment of NP cells with IL-1β in combination with CCN2 suppressed the inductive effect of IL-1β on catabolic genes, including MMP-3, ADAMTS-5, syndecan 4, and prolyl hydroxylase 3. Likewise, silencing of CCN2 in human NP cells resulted in elevated basal expression of several catabolic genes and inflammatory cytokines like IL-6, IL-4, and IL-12 as measured by gene expression and cytokine protein array, respectively. Interestingly, the suppressive effect of CCN2 on IL-1β was independent of modulation of NF-κB signaling. Using disintegrins, echistatin, and VLO4, peptide inhibitors to αvβ3 and α5β1 integrins, we showed that CCN2 binding to both integrins was required for the inhibition of IL-1β-induced catabolic gene expression. It is noteworthy that analysis of human tissues showed a trend of altered expression of these integrins during degeneration. Taken together, these results suggest that CCN2 and inflammatory cytokines form a functional negative feedback loop in NP cells that may be important in the pathogenesis of disc disease.
Keywords: Cartilage Biology; Chondrocytes; Cytokine; Extracellular Matrix Proteins; Integrins.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

