Vascular endothelial growth factor-C: its unrevealed role in fibrogenesis
- PMID: 24464750
- PMCID: PMC3949048
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpheart.00559.2013
Vascular endothelial growth factor-C: its unrevealed role in fibrogenesis
Abstract
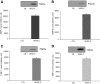
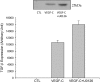
Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)-C is a key mediator of lymphangiogenesis. Our recent study shows that VEGF-C/VEGF receptors (VEGFR)-3 are significantly increased in the infarcted rat myocardium, where VEGFR-3 is expressed not only in lymph ducts but also in myofibroblasts, indicating that VEGF-C has an unrevealed role in fibrogenesis during cardiac repair. The current study is to explore the regulation and molecular mechanisms of VEGF-C in fibrogenesis. The potential regulation of VEGF-C on myofibroblast differentiation/growth/migration, collagen degradation/synthesis, and transforming growth factor (TGF)-β and ERK pathways was detected in cultured cardiac myofibroblasts. Our results showed that VEGF-C significantly increased myofibroblast proliferation, migration, and type I/III collagen production. Matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-2 and -9 were significantly elevated in the medium of VEGF-C-treated cells, coincident with increased tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase (TIMP)-1 and TIMP-2. Furthermore, VEGF-C activated the TGF-β1 pathway and ERK phosphorylation, which was significantly suppressed by TGF-β or ERK blockade. This is the first study indicating that in addition to lymphangiogenesis, VEGF-C is also involved in fibrogenesis through stimulation of myofibroblast proliferation, migration, and collagen synthesis, via activation of the TGF-β1 and ERK pathways.
Keywords: ERK; TGF-β1; VEGF-C; collagen degradation; collagen synthesis; myofibroblasts.
Figures





References
-
- Chaudary N, Milosevic M, Hill RP. Suppression of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 3 (VEGFR3) and vascular endothelial growth factor C (VEGFC) inhibits hypoxia-induced lymph node metastases in cervix cancer. Gynecol Oncol 123: 393–400, 2011 - PubMed
-
- Cohen S, Efraim AN, Levi-Schaffer F, Eliashar R. The effect of hypoxia and cycloxygenase inhibitors on nasal polyp derived fibroblasts. Am J Otolaryngol 32: 564–573, 2011 - PubMed
-
- Daskalopoulos EP, Hermans KC, Blankesteijn WM. Cardiac (myo)fibroblast: novel strategies for its targeting following myocardial infarction. Curr Pharm Des 2013. June 18 [Epub ahead of print] - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

