PAI-1 leads to G1-phase cell-cycle progression through cyclin D3/cdk4/6 upregulation
- PMID: 24464915
- PMCID: PMC4064567
- DOI: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-13-0543
PAI-1 leads to G1-phase cell-cycle progression through cyclin D3/cdk4/6 upregulation
Abstract
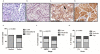
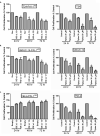
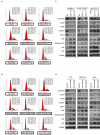
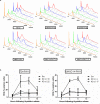
The canonical function of plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 (PAI-1/SERPINE1) is as an inhibitor of urokinase-type plasminogen activator for blood clot maintenance, but it is now also considered a pleiotropic factor that can exert diverse cellular and tumorigenic effects. However, the mechanism controlling its pleiotropic effects is far from being understood. To elucidate the tumorigenic role of PAI-1, we tested the effects of PAI-1 after manipulation of its expression or through the use of a small-molecule inhibitor, tiplaxtinin. Downregulation of PAI-1 significantly reduced cellular proliferation through an inability to progress from the G(0-G1) phase of the cell cycle. Accordingly, overexpression of PAI-1 augmented proliferation by encouraging S-phase entry. Biochemically, cell-cycle arrest was associated with the depletion of the G(1)-phase transition complexes, cyclin D3/cdk4/6 and cyclin E/cdk2, in parallel with the upregulation of the cell-cycle inhibitors p53, p21Cip1/Waf1, and p27Kip1. PAI-1 depletion significantly decreased the tumor size of urothelial T24 and UM-UC-14 xenografts, and overexpression of PAI-1 substantially increased the tumor size of HeLa xenografts. Finally, immunohistochemical analysis of human bladder and cervical tumor tissue microarrays revealed increased expression of PAI-1 in cancerous tissue, specifically in aggressive tumors, supporting the relevance of this molecule in human tumor biology.
Implications: Targeting PAI-1 has beneficial antitumoral effects and should be further investigated clinically.
Figures
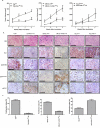
References
-
- Lee CC, Huang TS. Plasminogen Activator Inhibitor-1: The Expression, Biological Functions, and Effects on Tumorigenesis and Tumor Cell Adhesion and Migration. Journal of Cancer Molecules. 2005;1:25–36.
-
- Wilkins-Port CE, Freytag J, Higgins SP, Higgins PJ. PAI-1: A Multifunctional SERPIN with Complex Roles in Cell Signaling and Migration. Cell Communication Insights. 2010;3:1–10.
-
- Lijnen HR. Pleiotropic functions of plasminogen activator inhibitor-1. Thromb Haemost. 2005;3:35–45. - PubMed
-
- Jankun J, Keck RW, Skrzypczak-Jankun E, Swiercz R. Inhibitors of urokinase reduce size of prostate cancer xenografts in severe combined immunodeficient mice. Cancer Res. 1997;57:559–63. - PubMed
-
- McMahon GA, Petitclerc E, Stefansson S, Smith E, Wong MK, Westrick RJ, et al. Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 regulates tumor growth and angiogenesis. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:33964–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

