Priming Lexical Neighbors of Spoken Words: Effects of Competition and Inhibition
- PMID: 24465086
- PMCID: PMC3901307
- DOI: 10.1016/0749-596x(89)90009-0
Priming Lexical Neighbors of Spoken Words: Effects of Competition and Inhibition
Abstract
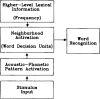
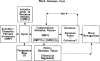
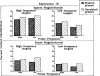
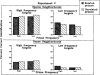
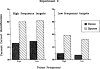
Two experiments employing an auditory priming paradigm were conducted to test predictions of the Neighborhood Activation Model of spoken word recognition (Luce & Pisoni, 1989, Neighborhoods of words in the mental lexicon. Manuscript under review). Acoustic-phonetic similarity, neighborhood densities, and frequencies of prime and target words were manipulated. In Experiment 1, priming with low frequency, phonetically related spoken words inhibited target recognition, as predicted by the Neighborhood Activation Model. In Experiment 2, the same prime-target pairs were presented with a longer inter-stimulus interval and the effects of priming were eliminated. In both experiments, predictions derived from the Neighborhood Activation Model regarding the effects of neighborhood density and word frequency were supported. The results are discussed in terms of competing activation of lexical neighbors and the dissociation of activation and frequency in spoken word recognition.
Figures


References
-
- Balota DA, Chumbley JI. Are lexical decisions a good measure of lexical access? The role of word frequency in the neglected decision stage. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Human Perception and Performance. 1984;10:340–357. - PubMed
-
- Becker CA, Killion TH. Interaction of visual and cognitive effects in word recognition. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Human Perception and Performance. 1977;3:389–401.
-
- Clark HH. The language-as-fixed-effect fallacy: A critique of language statistics in psychological research. Journal of Verbal Learning and Verbal Behavior. 1973;12:335–359.
-
- Collins A, Loftus E. A spreading activation theory of semantic processing. Psychological Review. 1975;82:407–428.
-
- Forster KI, Wales RJ, Walker E. New approaches to language mechanisms. North Holland; Amsterdam: 1976. Accessing the mental lexicon.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
