Inhibitory effect of N-ethyl-3-amino-5-oxo-4-phenyl-2,5-dihydro-1 H-pyrazole-1-carbothioamide on Haemophilus spp. planktonic or biofilm-forming cells
- PMID: 24465123
- PMCID: PMC3895188
- DOI: 10.1007/s00044-013-0700-7
Inhibitory effect of N-ethyl-3-amino-5-oxo-4-phenyl-2,5-dihydro-1 H-pyrazole-1-carbothioamide on Haemophilus spp. planktonic or biofilm-forming cells
Abstract
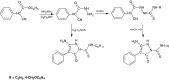
During this study, we have investigated in vitro activity of N-substituted-3-amino-5-oxo-4-phenyl-2,5-dihydro-1H-pyrazole-1-carbothioamide derivatives with N-ethyl, N-(4-metoxyphenyl) and N-cyclohexyl substituents against Gram-negative Haemophilus influenzae and H. parainfluenzae bacteria. A spectrophotometric assay was used in order to determine the bacterial growth and biofilm formation using a microtiter plate to estimate minimal inhibitory concentration (MIC) and minimal biofilm inhibitory concentration (MBIC). Among the tested N-substituted pyrazole derivatives, only N-ethyl-3-amino-5-oxo-4-phenyl-2,5-dihydro-1H-pyrazole-1-carbothioamide showed a significant in vitro activity against both planktonic cells of H. parainfluenzae (MIC = 0.49-31.25 μg ml-1) and H. influenzae (MIC = 0.24-31.25 μg ml-1) as well as biofilm-forming cells of H. parainfluenzae (MBIC = 0.24-31.25 μg ml-1) and H. influenzae (MBIC = 0.49 to ≥31.25 μg ml-1). The pyrazole compound exerted higher inhibitory effect both on the growth of planktonic cells and biofilm formation by penicillinase-positive and penicillinase-negative isolates of H. parainfluenzae than the activity of commonly used antibiotics such as ampicillin. No cytotoxicity of the tested compound in vitro at concentrations used was found. The tested pyrazole N-ethyl derivative could be considered as a compound for the design of agents active against both pathogenic H. influenzae and opportunistic H. parainfluenzae, showing also anti-biofilm activity. This appears important because biofilms are determinants of bacterial persistence in long-term and recurrent infections recalcitrant to standard therapy.
Keywords: Anti-biofilm activity; Antibacterial activity; Cytotoxicity; Haemophilus spp.; Pyrazole derivatives.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Nasopharyngeal and Adenoid Colonization by Haemophilus influenzae and Haemophilus parainfluenzae in Children Undergoing Adenoidectomy and the Ability of Bacterial Isolates to Biofilm Production.Medicine (Baltimore). 2015 May;94(18):e799. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000000799. Medicine (Baltimore). 2015. PMID: 25950686 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of Thiazolidine-2,4-Dione Derivatives with Azolidine or Thiosemicarbazone Moieties on Haemophilus spp. Planktonic or Biofilm-Forming Cells.Molecules. 2019 Mar 17;24(6):1051. doi: 10.3390/molecules24061051. Molecules. 2019. PMID: 30884874 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibitory effect of 1,2,4-triazole-ciprofloxacin hybrids on Haemophilus parainfluenzae and Haemophilus influenzae biofilm formation in vitro under stationary conditions.Res Microbiol. 2016 Oct;167(8):647-654. doi: 10.1016/j.resmic.2016.05.009. Epub 2016 Jun 10. Res Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 27292570
-
Synthesis and monoamine oxidase inhibitory activities of some 3-(4-fluorophenyl)-5-aryl-n-substituted-4,5-dihydro-(1H)-pyrazole-1-carbothioamide derivatives.Drug Res (Stuttg). 2014 Nov;64(11):591-8. doi: 10.1055/s-0033-1363997. Epub 2014 Jan 22. Drug Res (Stuttg). 2014. PMID: 24452523
-
Haemophilus parainfluenzae Strain ATCC 33392 Forms Biofilms In Vitro and during Experimental Otitis Media Infections.Infect Immun. 2017 Aug 18;85(9):e01070-16. doi: 10.1128/IAI.01070-16. Print 2017 Sep. Infect Immun. 2017. PMID: 28674033 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Nasopharyngeal and Adenoid Colonization by Haemophilus influenzae and Haemophilus parainfluenzae in Children Undergoing Adenoidectomy and the Ability of Bacterial Isolates to Biofilm Production.Medicine (Baltimore). 2015 May;94(18):e799. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000000799. Medicine (Baltimore). 2015. PMID: 25950686 Free PMC article.
-
The Association between Biofilm Formation and Antimicrobial Resistance with Possible Ingenious Bio-Remedial Approaches.Antibiotics (Basel). 2022 Jul 11;11(7):930. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics11070930. Antibiotics (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35884186 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Influence of Thiazolidine-2,4-Dione Derivatives with Azolidine or Thiosemicarbazone Moieties on Haemophilus spp. Planktonic or Biofilm-Forming Cells.Molecules. 2019 Mar 17;24(6):1051. doi: 10.3390/molecules24061051. Molecules. 2019. PMID: 30884874 Free PMC article.
-
Innovative Silica-Supported Acid Catalyst for Sustainable Synthesis of Bioactive Pyrazoles: Insights into Mechanisms and Applications.ACS Omega. 2025 May 8;10(19):19750-19763. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.5c00920. eCollection 2025 May 20. ACS Omega. 2025. PMID: 40415834 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Amer FAA, El-Behedy EM, Mohtady HA. New targets for antibacterial agents. Biol Rev Camb Philos Soc. 2008;3:46–57.
-
- Armbruster CE, Hong W, Pang B, Dew KE, Juneau RA, Byrd MS, Love CF, Kock ND, Swords EW. LuxS promotes biofilm maturation and persistence of nontypeable Haemophilus influenzae in vivo via modulation of lipooligosaccharides on the bacterial surface. Infect Immun. 2009;77:4081–4091. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00320-09. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
