Clinical and Pathological Features of Korean Patients with DNM2-Related Centronuclear Myopathy
- PMID: 24465259
- PMCID: PMC3896645
- DOI: 10.3988/jcn.2014.10.1.24
Clinical and Pathological Features of Korean Patients with DNM2-Related Centronuclear Myopathy
Abstract
Background and purpose: Centronuclear myopathy (CNM) is characterized by the presence of central nuclei within a large number of muscle fibers. Mutations of the dynamin 2 gene (DNM2) are common causes of autosomal dominant or sporadic CNM. The aim of this study was to characterize the clinical and pathological features of CNM relative to the presence of DNM2 mutations.
Methods: Six patients with clinical and pathological features of CNM were recruited. Detailed clinical and pathological findings were analyzed according to the presence of DNM2 mutations.
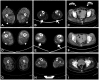
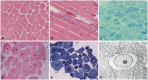
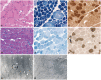
Results: We detected DNM2 mutations in four of the six sporadic CNM patients, and identified the following distinct clinical and pathological features in those patients with DNM2 mutations: preferential involvement of the distal lower limbs, typical nuclear centralization, and radially distributed sarcoplasmic strands in muscle pathology. In contrast, those without DNM2 mutations exhibited rather diffuse muscular involvement, and nuclear internalization and myofibrillar disorganization were more pronounced features of their muscle pathology.
Conclusions: These findings suggest the presence of specific features in Korean CNM patients. A detailed clinical and pathological examination of CNM patients would be helpful for molecular genetic analyses of this condition.
Keywords: DNM2; central nuclei; centronuclear myopathy; internal nuclei; muscle involvement; sarcoplasmic strands.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no financial conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Spiro AJ, Shy GM, Gonatas NK. Myotubular myopathy. Persistence of fetal muscle in an adolescent boy. Arch Neurol. 1966;14:1–14. - PubMed
-
- Laporte J, Hu LJ, Kretz C, Mandel JL, Kioschis P, Coy JF, et al. A gene mutated in X-linked myotubular myopathy defines a new putative tyrosine phosphatase family conserved in yeast. Nat Genet. 1996;13:175–182. - PubMed
-
- Bitoun M, Maugenre S, Jeannet PY, Lacène E, Ferrer X, Laforêt P, et al. Mutations in dynamin 2 cause dominant centronuclear myopathy. Nat Genet. 2005;37:1207–1209. - PubMed
-
- Nicot AS, Toussaint A, Tosch V, Kretz C, Wallgren-Pettersson C, Iwarsson E, et al. Mutations in amphiphysin 2 (BIN1) disrupt interaction with dynamin 2 and cause autosomal recessive centronuclear myopathy. Nat Genet. 2007;39:1134–1139. - PubMed
-
- Wilmshurst JM, Lillis S, Zhou H, Pillay K, Henderson H, Kress W, et al. RYR1 mutations are a common cause of congenital myopathies with central nuclei. Ann Neurol. 2010;68:717–726. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

