Both dietary supplementation with monosodium L-glutamate and fat modify circulating and tissue amino acid pools in growing pigs, but with little interactive effect
- PMID: 24465415
- PMCID: PMC3897369
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0084533
Both dietary supplementation with monosodium L-glutamate and fat modify circulating and tissue amino acid pools in growing pigs, but with little interactive effect
Abstract
Background: The Chinese population has undergone rapid transition to a high-fat diet. Furthermore, monosodium L-glutamate (MSG) is widely used as a daily food additive in China. Little information is available on the effects of oral MSG and dietary fat supplementation on the amino acid balance in tissues. The present study aimed to determine the effects of both dietary fat and MSG on amino acid metabolism in growing pigs, and to assess any possible interactions between these two nutrients.
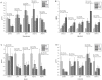
Methods and results: Four iso-nitrogenous and iso-caloric diets (basal diet, high fat diet, basal diet with 3% MSG and high fat diet with 3% MSG) were provided to growing pigs. The dietary supplementation with fat and MSG used alone and in combination were found to modify circulating and tissue amino acid pools in growing pigs. Both dietary fat and MSG modified the expression of gene related to amino acid transport in jejunum.
Conclusions: Both dietary fat and MSG clearly influenced amino acid content in tissues but in different ways. Both dietary fat and MSG enhance the absorption of amino acids in jejunum. However, there was little interaction between the effects of dietary fat and MSG.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

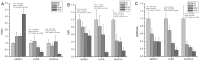
References
-
- Jinap S, Hajeb P (2010) Glutamate. Its applications in food and contribution to health. Appetite 55: 1–10. - PubMed
-
- Blachier F, Boutry C, Bos C, Tomé D (2009) Metabolism and functions of L-glutamate in the epithelial cells of the small and large intestines. Am J Clin Nutr 90 3: 814S–821S. - PubMed
-
- Rezaei R, Knabe DA, Tekwe CD, Dahanayaka S, Ficken MD, et al. (2013) Dietary supplementation with monosodium glutamate is safe and improves growth performance in post weaning pigs. Amino acids 44 3: 911–923. - PubMed
-
- Paddon-Jones D, Sheffield-Moore M, Zhang XJ, Volpi E, Wolf SE, et al. (2004) Amino acid ingestion improves muscle protein synthesis in the young and elderly. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 286: E321–E328. - PubMed
-
- Nakashima K, Ishida A, Yamazaki M, Abe H (2005) Leucine suppresses myofibrillar proteolysis by down-regulating ubiquitin-proteasome pathway in chick skeletal muscles. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 336: 660–666. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

