Interleukin-4-mediated 15-lipoxygenase-1 trans-activation requires UTX recruitment and H3K27me3 demethylation at the promoter in A549 cells
- PMID: 24465480
- PMCID: PMC3896354
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0085085
Interleukin-4-mediated 15-lipoxygenase-1 trans-activation requires UTX recruitment and H3K27me3 demethylation at the promoter in A549 cells
Erratum in
- PLoS One. 2014;9(2):e91499
Abstract
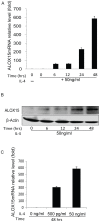
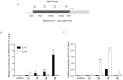
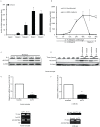
Arachidonate 15-lipoxygenase-1 (ALOX15) oxygenates polyunsaturated fatty acids and bio-membranes, generating multiple lipid signalling mediators involved in inflammation. Several lines of evidence indicate that ALOX15 activation in the respiratory tract contributes to asthma progression. Recent experimental data reveals that histone modification at the promoter plays a critical role in ALOX15 gene transcription. In the present study, we examined the status of histone H3 trimethyl-lysine 27 (H3K27me3) at the ALOX15 promoter by chromatin immunoprecipitation assay in human lung epithelial carcinoma A549 cells incubated with or without interleukin (IL)-4. We identified demethylation of H3K27me3 at the ALOX15 promoter after IL-4 treatment. Furthermore, we found that the H3K27me2/3-specific demethylase, ubiquitously transcribed tetratricopeptide repeat, X chromosome (UTX), mediates the H3K27me3 demethylation during ALOX15 transcriptional activation. When UTX expression was knocked down using siRNA, IL-4-mediated H3K27me3 demethylation and ALOX15 induction were significantly attenuated. The critical role of UTX in ALOX15 expression was confirmed in human monocytes and the Hodgkin lymphoma (HL) cell line L1236, but was in these cells not related to H3K27me3-demethylase activity. These results demonstrate that UTX is implicated in IL-4 mediated transcriptional activation of the ALOX15 gene.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Claesson HE (2009) On the biosynthesis and biological role of eoxins and 15-lipoxygenase-1 in airway inflammation and Hodgkin lymphoma. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat 89: 120–125. - PubMed
-
- Nassar GM, Morrow JD, Roberts LJ 2nd, Lakkis FG, Badr KF (1994) Induction of 15-lipoxygenase by interleukin-13 in human blood monocytes. J? Biol Chem 269: 27631–27634. - PubMed
-
- Schewe T (2002) 15-lipoxygenase-1: a prooxidant enzyme. Biol Chem 383: 365–374. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

