MicroRNA 135a suppresses lymph node metastasis through down-regulation of ROCK1 in early gastric cancer
- PMID: 24465504
- PMCID: PMC3897422
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0085205
MicroRNA 135a suppresses lymph node metastasis through down-regulation of ROCK1 in early gastric cancer
Abstract
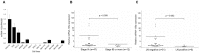
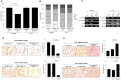
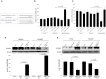
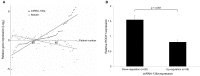
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) play a critical role in gastric cancer progression and metastasis. This study investigated the role of miRNA-135a in early gastric cancer (EGC) including lymph node (LN) metastasis. We examined the correlation between miRNA-135a expression and clinical outcomes in 59 patients who underwent surgery for EGC. Using gastric cancer cell lines, we performed functional and target gene analyses. miRNA-135a expression was down-regulated in 33.9% of patients. These patients showed a significantly more advanced stage (TNM stage ≥ IB, 35.0% vs. 12.8%, p = 0.045) and higher rate of LN metastasis (30.0% vs. 5.1%, p = 0.014) than those with up-regulation of miRNA-135a expression. In a multivariate analysis, down-regulation of miRNA-135a was an independent risk factor for LN metastasis (adjusted odds ratio, 8.04; 95% confidence interval, 1.08-59.81; p = 0.042). Functional analyses using gastric cancer cell lines showed that miRNA-135a suppressed cell viability, epithelial-mesenchymal transition, cell invasion, and migration. ROCK1 was a target of miRNA-135a and its expression was inversely correlated to that of miRNA-135a. ROCK1 expression was significantly increased in EGC patients with LN metastasis than in those without LN metastasis. Our results confirm the tumor-suppressive role of miRNA-135a, and demonstrate its role in LN metastasis in EGC. miRNA-135a and its target gene ROCK1 may be novel therapeutic and prognostic targets for EGC.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Ferlay J, Shin HR, Bray F, Forman D, Mathers C, et al. (2010) Estimates of worldwide burden of cancer in 2008: GLOBOCAN 2008. Int J Cancer 127: 2893–2917. - PubMed
-
- Borie F, Millat B, Fingerhut A, Hay JM, Fagniez PL, et al. (2000) Lymphatic involvement in early gastric cancer: prevalence and prognosis in France. Arch Surg 135: 1218–1223. - PubMed
-
- Roviello F, Rossi S, Marrelli D, Pedrazzani C, Corso G, et al. (2006) Number of lymph node metastases and its prognostic significance in early gastric cancer: a multicenter Italian study. J Surg Oncol 94: 275–280. - PubMed
-
- An JY, Baik YH, Choi MG, Noh JH, Sohn TS, et al. (2007) Predictive factors for lymph node metastasis in early gastric cancer with submucosal invasion: analysis of a single institutional experience. Ann Surg 246: 749–753. - PubMed
-
- Gotoda T, Yanagisawa A, Sasako M, Ono H, Nakanishi Y, et al. (2000) Incidence of lymph node metastasis from early gastric cancer: estimation with a large number of cases at two large centers. Gastric Cancer 3: 219–225. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

