Binding of HSV-1 glycoprotein K (gK) to signal peptide peptidase (SPP) is required for virus infectivity
- PMID: 24465545
- PMCID: PMC3896391
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0085360
Binding of HSV-1 glycoprotein K (gK) to signal peptide peptidase (SPP) is required for virus infectivity
Abstract
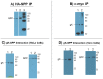
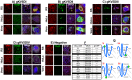
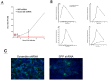
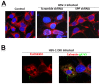
Glycoprotein K (gK) is a virion envelope protein of herpes simplex virus types 1 (HSV-1) and 2 (HSV-2), which plays important roles in virion entry, morphogenesis and egress. Two-hybrid and pull-down assays were utilized to demonstrate that gK and no other HSV-1 genes specifically binds to signal peptide peptidase (SPP), also known as minor histocompatibility antigen H13. SPP dominant negative mutants, shRNA against SPP significantly reduced HSV-1 replication in vitro. SPP also affected lysosomes and ER responses to HSV-1 infection. Thus, in this study we have shown for the first time that gK, despite its role in fusion and egress, is also involved in binding the cytoplasmic protein SPP. These results also suggest that SPP plays an important role in viral replication and possibly virus pathogenesis. This makes SPP unique in that its function appears to be required by the virus as no other protein can compensate its loss in terms of viral replication.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Weihofen A, Binns K, Lemberg MK, Ashman K, Martoglio B (2002) Identification of signal peptide peptidase, a presenilin-type aspartic protease. Science 296: 2215–2218. - PubMed
-
- Lemberg MK, Martoglio B (2002) Requirements for signal peptide peptidase-catalyzed intramembrane proteolysis. Mol Cell 10: 735–744. - PubMed
-
- Sun H, Liu J, Ding F, Wang X, Liu M, et al. (2006) Investigation of differentially expressed proteins in rat gastrocnemius muscle during denervation-reinnervation. J Muscle Res Cell Motil 27: 241–250. - PubMed
-
- Bolhuis A, Matzen A, Hyyrylainen HL, Kontinen VP, Meima R, et al. (1999) Signal peptide peptidase- and ClpP-like proteins of Bacillus subtilis required for efficient translocation and processing of secretory proteins. J Biol Chem 274: 24585–24592. - PubMed
-
- Yan G, Zhang G, Fang X, Zhang Y, Li C, et al. (2011) Genome sequencing and comparison of two nonhuman primate animal models, the cynomolgus and Chinese rhesus macaques. Nat Biotechnol 29: 1019–1023. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

