Pch2 prevents Mec1/Tel1-mediated Hop1 phosphorylation occurring independently of Red1 in budding yeast meiosis
- PMID: 24465650
- PMCID: PMC3897485
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0085687
Pch2 prevents Mec1/Tel1-mediated Hop1 phosphorylation occurring independently of Red1 in budding yeast meiosis
Abstract
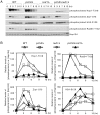
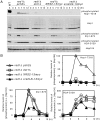
A prominent feature of meiosis in most sexually reproducing organisms is interhomolog recombination whereby a significant fraction of the programmed meiotic double-strand breaks are repaired using intact homologous non-sister chromatids rather than sister chromatids. Budding yeast DNA damage checkpoint kinases Mec1 and Tel1 act together with the axial element protein Red1 to promote interhomolog recombination by phosphorylating another axial element protein Hop1. Mec1 and Tel1 also phosphorylate γH2A and the synaptonemal complex protein Zip1 independently of Red1 to facilitate premeiotic DNA replication and to destabilize homology-independent centromere pairing, respectively. It has been unclear why Hop1 phosphorylation is Red1-dependent. Here, we report that the pachytene checkpoint protein 2 (Pch2) specifically prevents Red1-independent Hop1 phosphorylation. Our findings reveal a new function for Pch2 in linking two axial element proteins Red1 and Hop1 thus coordinating their effects in meiotic recombination and the checkpoint network.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Three distinct modes of Mec1/ATR and Tel1/ATM activation illustrate differential checkpoint targeting during budding yeast early meiosis.Mol Cell Biol. 2013 Aug;33(16):3365-76. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00438-13. Epub 2013 Jun 17. Mol Cell Biol. 2013. PMID: 23775120 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphorylation of the axial element protein Hop1 by Mec1/Tel1 ensures meiotic interhomolog recombination.Cell. 2008 Mar 7;132(5):758-70. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2008.01.035. Cell. 2008. PMID: 18329363
-
Mek1 stabilizes Hop1-Thr318 phosphorylation to promote interhomolog recombination and checkpoint responses during yeast meiosis.Nucleic Acids Res. 2012 Dec;40(22):11416-27. doi: 10.1093/nar/gks920. Epub 2012 Oct 9. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012. PMID: 23047948 Free PMC article.
-
Budding yeast Rad51: a paradigm for how phosphorylation and intrinsic structural disorder regulate homologous recombination and protein homeostasis.Curr Genet. 2021 Jun;67(3):389-396. doi: 10.1007/s00294-020-01151-2. Epub 2021 Jan 12. Curr Genet. 2021. PMID: 33433732 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interplays between ATM/Tel1 and ATR/Mec1 in sensing and signaling DNA double-strand breaks.DNA Repair (Amst). 2013 Oct;12(10):791-9. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2013.07.009. Epub 2013 Aug 13. DNA Repair (Amst). 2013. PMID: 23953933 Review.
Cited by
-
Phospho-Regulation of Meiotic Prophase.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Apr 13;9:667073. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.667073. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 33928091 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Meiotic prophase length modulates Tel1-dependent DNA double-strand break interference.PLoS Genet. 2024 Mar 1;20(3):e1011140. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1011140. eCollection 2024 Mar. PLoS Genet. 2024. PMID: 38427688 Free PMC article.
-
The meiotic checkpoint network: step-by-step through meiotic prophase.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2014 Oct 1;6(10):a016675. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a016675. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2014. PMID: 25274702 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pch2(TRIP13): controlling cell division through regulation of HORMA domains.Chromosoma. 2015 Sep;124(3):333-9. doi: 10.1007/s00412-015-0516-y. Epub 2015 Apr 21. Chromosoma. 2015. PMID: 25895724 Review.
-
Role of TRIP13 in human cancer development.Mol Biol Rep. 2024 Oct 22;51(1):1088. doi: 10.1007/s11033-024-10012-x. Mol Biol Rep. 2024. PMID: 39436503 Review.
References
-
- Gobbini E, Cesena D, Galbiati A, Lockhart A, Longhese MP (2013) Interplays between ATM/Tel1 and ATR/Mec1 in sensing and signaling DNA double-strand breaks. DNA Repair 12: 791–799. - PubMed
-
- Carballo JA, Cha RS (2007) Meiotic roles of Mec1, a budding yeast homolog of mammalian ATR/ATM. Chromosome Res 15: 539–550. - PubMed
-
- Roeder GS (1997) Meiotic chromosomes: it takes two to tango. Genes Dev 11: 2600–2621. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

