NOS2 is critical to the development of emphysema in Sftpd deficient mice but does not affect surfactant homeostasis
- PMID: 24465666
- PMCID: PMC3897517
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0085722
NOS2 is critical to the development of emphysema in Sftpd deficient mice but does not affect surfactant homeostasis
Abstract
Rationale: Surfactant protein D (SP-D) has important immuno-modulatory properties. The absence of SP-D results in an inducible NO synthase (iNOS, coded by NOS2 gene) related chronic inflammation, development of emphysema-like pathophysiology and alterations of surfactant homeostasis.
Objective: In order to test the hypothesis that SP-D deficiency related abnormalities in pulmonary structure and function are a consequence of iNOS induced inflammation, we generated SP-D and iNOS double knockout mice (DiNOS).
Methods: Structural data obtained by design-based stereology to quantify the emphysema-like phenotype and disturbances of the intracellular surfactant were correlated to invasive pulmonary function tests and inflammatory markers including activation markers of alveolar macrophages and compared to SP-D (Sftpd(-/-)) and iNOS single knockout mice (NOS2(-/-)) as well as wild type (WT) littermates.
Measurements and results: DiNOS mice had reduced inflammatory cells in BAL and BAL-derived alveolar macrophages showed an increased expression of markers of an alternative activation as well as reduced inflammation. As evidenced by increased alveolar numbers and surface area, emphysematous changes were attenuated in DiNOS while disturbances of the surfactant system remained virtually unchanged. Sftpd(-/-) demonstrated alterations of intrinsic mechanical properties of lung parenchyma as shown by reduced stiffness and resistance at its static limits, which could be corrected by additional ablation of NOS2 gene in DiNOS.
Conclusion: iNOS related inflammation in the absence of SP-D is involved in the emphysematous remodeling leading to a loss of alveoli and associated alterations of elastic properties of lung parenchyma while disturbances of surfactant homeostasis are mediated by different mechanisms.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
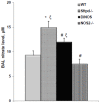


 (typeII)) is present in Sftpd−/− and DiNOS to a similar extent (A). The increased volume of lamellar bodies per lung V(lb,lung) (B) is unaffected by the additional ablation of the NOS2-gene in Sftpd deficient mice. Data shown are mean and individual data, n = 5–6 animals per genotype. Statistically significant differences between groups are shown in Table 3.
(typeII)) is present in Sftpd−/− and DiNOS to a similar extent (A). The increased volume of lamellar bodies per lung V(lb,lung) (B) is unaffected by the additional ablation of the NOS2-gene in Sftpd deficient mice. Data shown are mean and individual data, n = 5–6 animals per genotype. Statistically significant differences between groups are shown in Table 3.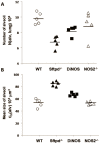
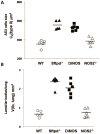
 (alv) (B) is decreased in the DiNOS mice compared to Sftpd−/− mice, indicating an attenuation of the pulmonary emphysema due to the additional ablation of the iNOS-gene in Sftpd deficient mice. Data shown are mean and individual data, n = 5–6 animals per genotype. Statistically significant differences between groups are shown in Table 2.
(alv) (B) is decreased in the DiNOS mice compared to Sftpd−/− mice, indicating an attenuation of the pulmonary emphysema due to the additional ablation of the iNOS-gene in Sftpd deficient mice. Data shown are mean and individual data, n = 5–6 animals per genotype. Statistically significant differences between groups are shown in Table 2.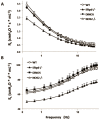


References
-
- LeVine A, Whitsett J, Hartshorn K, Crouch E, Korfhagen T (2001) Surfactant protein D enhances clearance of influenza A virus from the lung in vivo. J Immunol 167: 5868–5873. - PubMed
-
- Wright J (2005) Immunoregulatory functions of surfactant proteins. Nat Rev Immunol 5: 58–68. - PubMed
-
- Gardai S, Xiao Y, Dickinson M, Nick J, Voelker D, et al. (2003) By binding SIRPalpha or calreticulin/CD91, lung collectins act as dual function surveillance molecules to suppress or enhance inflammation. Cell 115: 13–23. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

