Chemo-immunotherapy with oxaliplatin and interleukin-7 inhibits colon cancer metastasis in mice
- PMID: 24465710
- PMCID: PMC3897491
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0085789
Chemo-immunotherapy with oxaliplatin and interleukin-7 inhibits colon cancer metastasis in mice
Abstract
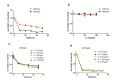
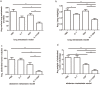
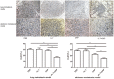
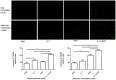
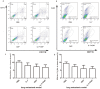
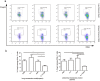
Combination of immunotherapy and chemotherapy has shown promise for cancer. Interleukin-7 (IL-7) can potentially enhance immune responses against tumor, while oxaliplatin (OXP), a platinum-based drug, can promote a favorable immune microenvironment and stimulate anticancer immune responses. We evaluated the anti-tumor activity of IL-7 combining OXP against a murine colon carcinoma in vitro and in vivo and studied the tumor immune microenvironment to investigate whether the combined treatment affects on the local immune cell populations. Utilizing lung and abdomen metastasis models by inoculation of CT26 mice colon cancer cells, we evaluated the anti-tumor efficacy of combining IL-7 and OXP in mice models. Tumor immune microenvironment was evaluated by flow cytometric analysis and immunohistochemical staining. Our study showed that the in vivo administration of IL-7 combined with OXP markedly inhibited the growth of tumors in lung and abdomen metastasis models of colon cancer. IL-7 alone had no effect on tumor growth in mice and IL-7 did not alter cell sensitivity to OXP in culture. The antitumor effect of combining IL-7 and OXP correlated with a marked increase in the number of tumor-infiltrating activated CD8+ T cells and a marked decrease in the number of regulatory T (Treg) cells in spleen. Our data suggest that OXP plus IL-7 treatment inhibits tumor cell growth by immunoregulation rather than direct cytotoxicity. Our findings justify further evaluation of combining IL-7 and chemotherapy as a novel experimental cancer therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



Similar articles
-
Intraperitoneal oxaliplatin administration inhibits the tumor immunosuppressive microenvironment in an abdominal implantation model of colon cancer.Mol Med Rep. 2018 Aug;18(2):2335-2341. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2018.9219. Epub 2018 Jun 25. Mol Med Rep. 2018. PMID: 29956798
-
Immunogenic death of colon cancer cells treated with oxaliplatin.Oncogene. 2010 Jan 28;29(4):482-91. doi: 10.1038/onc.2009.356. Epub 2009 Nov 2. Oncogene. 2010. PMID: 19881547
-
Synergistic antitumor effect of anti-PD-L1 combined with oxaliplatin on a mouse tumor model.J Cell Physiol. 2019 Nov;234(11):19866-19874. doi: 10.1002/jcp.28585. Epub 2019 Apr 2. J Cell Physiol. 2019. PMID: 30941773
-
Anti-cancer Therapies Employing IL-2 Cytokine Tumor Targeting: Contribution of Innate, Adaptive and Immunosuppressive Cells in the Anti-tumor Efficacy.Front Immunol. 2018 Dec 18;9:2905. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.02905. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 30619269 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Anticancer immunotherapy using inactivated Sendai virus particles].Uirusu. 2007 Jun;57(1):19-27. doi: 10.2222/jsv.57.19. Uirusu. 2007. PMID: 18040151 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
Systemic immune response induced by oxaliplatin-based neoadjuvant therapy favours survival without metastatic progression in high-risk rectal cancer.Br J Cancer. 2018 May;118(10):1322-1328. doi: 10.1038/s41416-018-0085-y. Epub 2018 Apr 26. Br J Cancer. 2018. PMID: 29695770 Free PMC article.
-
The Impact of Chemotherapy, Radiation and Epigenetic Modifiers in Cancer Cell Expression of Immune Inhibitory and Stimulatory Molecules and Anti-Tumor Efficacy.Vaccines (Basel). 2016 Nov 14;4(4):43. doi: 10.3390/vaccines4040043. Vaccines (Basel). 2016. PMID: 27854240 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immunogenic Chemotherapy Sensitizes Tumors to Checkpoint Blockade Therapy.Immunity. 2016 Feb 16;44(2):343-54. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2015.11.024. Epub 2016 Feb 9. Immunity. 2016. PMID: 26872698 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of the immune cell landscape in CRC: Clinical implications of tumour-infiltrating leukocytes in early- and late-stage CRC.Front Immunol. 2023 Feb 8;13:978862. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.978862. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 36846019 Free PMC article.
-
Liposomal β-Sitosterol Suppresses Metastasis of CT26/luc Colon Carcinoma via Inhibition of MMP-9 and Evoke of Immune System.Pharmaceutics. 2022 Jun 7;14(6):1214. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14061214. Pharmaceutics. 2022. PMID: 35745788 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Tesniere A, Schlemmer F, Boige V, Kepp O, Martins I, et al. (2010) Immunogenic death of colon cancer cells treated with oxaliplatin. Oncogene 29: 482–491. - PubMed
-
- Gonzalez-Aparicio M, Alzuguren P, Mauleon I, Medina-Echeverz J, Hervas-Stubbs S, et al. (2011) Oxaliplatin in combination with liver-specific expression of interleukin 12 reduces the immunosuppressive microenvironment of tumours and eradicates metastatic colorectal cancer in mice. Gut 60: 341–349. - PubMed
-
- Fry TJ, Connick E, Falloon J, Lederman MM, Liewehr DJ, et al. (2001) A potential role for interleukin-7 in T-cell homeostasis. Blood 97: 2983–2990. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

