Angiopoietin-like 4 confers resistance to hypoxia/serum deprivation-induced apoptosis through PI3K/Akt and ERK1/2 signaling pathways in mesenchymal stem cells
- PMID: 24465718
- PMCID: PMC3897528
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0085808
Angiopoietin-like 4 confers resistance to hypoxia/serum deprivation-induced apoptosis through PI3K/Akt and ERK1/2 signaling pathways in mesenchymal stem cells
Retraction in
-
Retraction: Angiopoietin-Like 4 Confers Resistance to Hypoxia/Serum Deprivation-Induced Apoptosis through PI3K/Akt and ERK1/2 Signaling Pathways in Mesenchymal Stem Cells.PLoS One. 2018 Mar 12;13(3):e0194448. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0194448. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 29529060 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
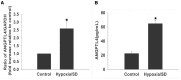
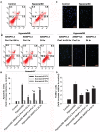
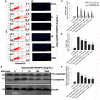
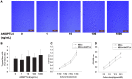
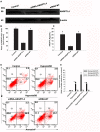
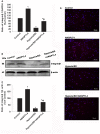
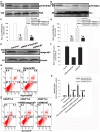
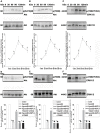
Angiopoietin-like 4 (ANGPTL4) is a potential anti-apoptotic agent for various cells. We examined the protective effect of ANGPTL4 on hypoxia/serum deprivation (SD)-induced apoptosis of MSCs, as well as the possible mechanisms. MSCs were obtained from rat bone marrow and cultured in vitro. Apoptosis was induced by hypoxia/SD for up to 24 hr, and assessed by flow cytometry and TUNEL assay. Expression levels of Akt, ERK1/2, focal adhesion kinase (FAK), Src, Bcl-2, Bax, cytochrome C and cleaved caspase-3 were detected by Western blotting. Integrin β1 mRNA was detected by qRT-PCR. Mitochondrial membrane potential was assayed using a membrane-permeable dye. Hypoxia/SD-induced apoptosis was significantly attenuated by recombinant rat ANGPTL4 in a concentration dependent manner. Moreover, ANGPTL4 decreased the hypoxia/SD-induced caspase-3 cleavage and the cytochrome C release, but increased the Bcl-2/Bax ratio and the mitochondrial membrane potential. Decreased expression of integrin β1, the ANGPTL4 receptor was observed during hypoxia/SD conditions, however, such decrease was reversed by ANGPTL4. In addition, ANGPTL4 induced integrin β1-associated FAK and Src phosphorylation, which was blocked by anti-integrin β1 antibody. ANGPTL4 also reversed the hypoxia/SD-induced decrease of Akt and ERK 1/2 phosphorylation, and the effect of ANGPTL4 was abolished by inhibitors of either integrins, ERK1/2, or phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K). Blocking integrinβ1, Akt or ERK largely attenuated anti-apoptotic effect of ANGPTL4. ANGPTL4 protects MSCs from hypoxia/SD-induced apoptosis by interacting with integrins to stimulate FAK complex, leading to downstream ERK1/2 and PI3K/Akt signaling pathways and mimicking the pathway in which MSCs contact with the extracellular matrix.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
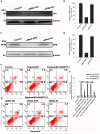
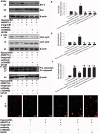
Similar articles
-
Lovastatin protects mesenchymal stem cells against hypoxia- and serum deprivation-induced apoptosis by activation of PI3K/Akt and ERK1/2.J Cell Biochem. 2008 Jan 1;103(1):256-69. doi: 10.1002/jcb.21402. J Cell Biochem. 2008. PMID: 17497701
-
SDF-1α inhibits hypoxia and serum deprivation-induced apoptosis in mesenchymal stem cells through PI3K/Akt and ERK1/2 signaling pathways.Mol Biol Rep. 2011 Jan;38(1):9-16. doi: 10.1007/s11033-010-0071-9. Epub 2010 Apr 10. Mol Biol Rep. 2011. PMID: 20383584
-
C1q tumor necrosis factor-related protein-3 protects mesenchymal stem cells against hypoxia- and serum deprivation-induced apoptosis through the phosphoinositide 3-kinase/Akt pathway.Int J Mol Med. 2014 Jan;33(1):97-104. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2013.1550. Epub 2013 Nov 7. Int J Mol Med. 2014. PMID: 24212403
-
Overexpressing cellular repressor of E1A-stimulated genes protects mesenchymal stem cells against hypoxia- and serum deprivation-induced apoptosis by activation of PI3K/Akt.Apoptosis. 2010 Apr;15(4):463-73. doi: 10.1007/s10495-009-0434-7. Apoptosis. 2010. PMID: 19997978
-
Exercise-induced signaling pathways to counteracting cardiac apoptotic processes.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Aug 11;10:950927. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.950927. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 36036015 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The combination of three-dimensional and rotary cell culture system promotes the proliferation and maintains the differentiation potential of rat BMSCs.Sci Rep. 2017 Mar 15;7(1):192. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-00087-x. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28298644 Free PMC article.
-
Suppression of A549 cell proliferation and metastasis by calycosin via inhibition of the PKC‑α/ERK1/2 pathway: An in vitro investigation.Mol Med Rep. 2015 Dec;12(6):7992-8002. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2015.4449. Epub 2015 Oct 15. Mol Med Rep. 2015. PMID: 26498639 Free PMC article.
-
Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells Attenuate Mitochondria Damage Induced by Hypoxia in Mouse Trophoblasts.PLoS One. 2016 Apr 21;11(4):e0153729. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0153729. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27100996 Free PMC article.
-
Factors affecting directional migration of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells to the injured spinal cord.Neural Regen Res. 2014 Sep 15;9(18):1688-95. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.141804. Neural Regen Res. 2014. PMID: 25374590 Free PMC article.
-
Macrophage migration inhibitory factor protects bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells from hypoxia/ischemia-induced apoptosis by regulating lncRNA MEG3.J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2022 Dec 15;23(12):989-1001. doi: 10.1631/jzus.B2200110. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2022. PMID: 36518052 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lopez AD, Mathers CD, Ezzati M, Jamison DT, Murray CJ (2006) Global and regional burden of disease and risk factors, 2001: systematic analysis of population health data. Lancet 367: 1747–1757. - PubMed
-
- Orlic D, Kajstura J, Chimenti S, Jakoniuk I, Anderson SM, et al. (2001) Bone marrow cells regenerate infarcted myocardium. Nature 410: 701–705. - PubMed
-
- Stamm C, Westphal B, Kleine HD, Petzsch M, Kittner C, et al. (2003) Autologous bone-marrow stem-cell transplantation for myocardial regeneration. Lancet 361: 45–46. - PubMed
-
- Wollert KC, Meyer GP, Lotz J, Ringes-Lichtenberg S, Lippolt P, et al. (2004) Intracoronary autologous bone-marrow cell transfer after myocardial infarction: the BOOST randomised controlled clinical trial. Lancet 364: 141–148. - PubMed
-
- Hahn JY, Cho HJ, Kang HJ, Kim TS, Kim MH, et al. (2008) Pre-treatment of mesenchymal stem cells with a combination of growth factors enhances gap junction formation, cytoprotective effect on cardiomyocytes, and therapeutic efficacy for myocardial infarction. J Am Coll Cardiol 51: 933–943. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

