Biomarkers of TGF-β signaling pathway and prognosis of pancreatic cancer
- PMID: 24465802
- PMCID: PMC3896410
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0085942
Biomarkers of TGF-β signaling pathway and prognosis of pancreatic cancer
Abstract
Background: Transforming growth factor (TGF)-β signaling pathway, may act both as a tumor suppressor and as a tumor promoter in pancreatic cancer, depending on tumor stage and cellular context. TGF-β pathway has been under intensive investigation as a potential therapeutic target in the treatment of cancer. We hypothesized a correlation between TGF-βR2/SMAD4 expression in the tumor, plasma TGF-β1 ligand level, genetic variation in TGF-B pathway and prognosis of pancreatic cancer.
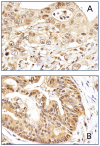
Method: We examined TGF-βR2 and SMAD4 protein expression in biopsy or surgical samples from 91 patients with pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) using immunohistochemistry. Plasma level of TGF-β1 was measured in 644 patients with PDAC using ELISA. Twenty-eight single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNP) of the TGF-β1, TGF-β2, TGF-β3, TGF-βR1, TGF-βR2, and SMAD4 genes were determined in 1636 patients with PDAC using the Sequenom method. Correlation between protein expression in the tumor, plasma TGF-β1 level, and genotypes with overall survival (OS) was evaluated with Cox proportional regression models.
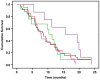
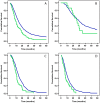
Results: The expression level of TGF-βR2 and SMAD4 as an independent marker was not associated with OS. However, patients with both low nuclear staining of TGF-βR2 and high nuclear staining of SMAD4 may have better survival (P = 0.06). The mean and median level of TGF-β1 was 15.44 (SD: 10.99) and 12.61 (interquartile range: 8.31 to 19.04) ng/ml respectively. Patients with advanced disease and in the upper quartile range of TGF-β1 level had significantly reduced survival than those with low levels (P = 0.02). A significant association of SMAD4 SNP rs113545983 with overall survival was observed (P<0.0001).
Conclusion: Our data provides valuable baseline information regarding the TGF-β pathway in pancreatic cancer, which can be utilized in targeted therapy clinical trials. High TGF-β1 plasma level, SMAD4 SNP or TGF-βR2/SMAD4 tumor protein expression may suggest a dependence on this pathway in patients with advanced pancreatic cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Bernabeu C, Lopez-Novoa JM, Quintanilla M (2009) The emerging role of TGF-beta superfamily coreceptors in cancer. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta 1792: 954–973. - PubMed
-
- Joshi A, Cao D (2010) TGF-beta signaling, tumor microenvironment and tumor progression: the butterfly effect. Frontiers in Bioscience 15: 180–194. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

