ARP2, a novel pro-apoptotic protein expressed in epithelial prostate cancer LNCaP cells and epithelial ovary CHO transformed cells
- PMID: 24465888
- PMCID: PMC3899214
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0086089
ARP2, a novel pro-apoptotic protein expressed in epithelial prostate cancer LNCaP cells and epithelial ovary CHO transformed cells
Abstract
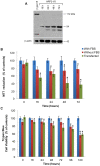
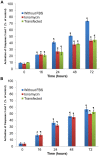
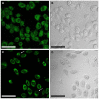
Neoplastic epithelial cells generate the most aggressive types of cancers such as those located in the lung, breast, colon, prostate and ovary. During advanced stages of prostate cancer, epithelial cells are associated to the appearance of androgen-independent tumors, an apoptotic-resistant phenotype that ultimately overgrows and promotes metastatic events. We have previously identified and electrophysiologically characterized a novel Ca(2+)-permeable channel activated during apoptosis in the androgen-independent prostate epithelial cancer cell line, LNCaP. In addition, we reported for the first time the cloning and characterization of this channel-like molecule named apoptosis regulated protein 2 (ARP2) associated to a lethal influx of Ca(2+) in Xenopus oocytes. In the present study, LNCaP cells and Chinese hamster ovary cells (CHO cell line) transfected with arp2-cDNA are induced to undergo apoptosis showing an important impact on cell viability and activation of caspases 3 and 7 when compared to serum deprived grown cells and ionomycin treated cells. The subcellular localization of ARP2 in CHO cells undergoing apoptosis was studied using confocal microscopy. While apoptosis progresses, ARP2 initially localized in the peri-nuclear region of cells migrates with time towards the plasma membrane region. Based on the present results and those of our previous studies, the fact that ARP2 constitutes a novel cation channel is supported. Therefore, ARP2 becomes a valuable target to modulate the influx and concentration of calcium in the cytoplasm of epithelial cancer cells showing an apoptotic-resistant phenotype during the onset of an apoptotic event.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
Discovery of the ARP2 protein as a determining molecule in tumor cell death.Gac Med Mex. 2019;155(5):504-510. doi: 10.24875/GMM.M20000340. Gac Med Mex. 2019. PMID: 32091029
-
Descubrimiento de la proteína reguladora de apoptosis 2 como determinante en la muerte de células tumorales.Gac Med Mex. 2019;155(5):546-553. doi: 10.24875/GMM.19005186. Gac Med Mex. 2019. PMID: 31695224
-
ARP2 a novel protein involved in apoptosis of LNCaP cells shares a high degree homology with splicing factor Prp8.Mol Cell Biochem. 2005 Jan;269(1-2):189-201. doi: 10.1007/s11010-005-3084-2. Mol Cell Biochem. 2005. PMID: 15786732
-
Fas Activated Serine-Threonine Kinase Domains 2 (FASTKD2) mediates apoptosis of breast and prostate cancer cells through its novel FAST2 domain.BMC Cancer. 2014 Nov 20;14:852. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-14-852. BMC Cancer. 2014. PMID: 25409762 Free PMC article.
-
Overexpression of bcl-2 protects prostate cancer cells from apoptosis in vitro and confers resistance to androgen depletion in vivo.Cancer Res. 1995 Oct 1;55(19):4438-45. Cancer Res. 1995. PMID: 7671257
References
-
- Wu X, Jin C, Wang F, Yu C, McKeehan WL (2003) Stromal cell heterogeneity in fibroblast growth factor-mediated stromal-epithelial cell cross-talk in premalignant prostate tumors. Cancer Res 63: 4936–4944. - PubMed
-
- Lopaczynski W, Hruszkewycz AM, Lieberman R (2001) Preprostatectomy: A clinical model to study stromal-epithelial interactions. Urology 57: 194–199. - PubMed
-
- Peehl DM (2005) Primary cell cultures as models of prostate cancer development. Endocr Relat Cancer 12: 19–47. - PubMed
-
- Chung LW, Hsieh CL, Law A, Sung SY, Gardner TA, et al. (2003) New targets for therapy in prostate cancer: modulation of stromal-epithelial interactions. Urology 62: 44–54. - PubMed
-
- Sung SY, Chung LW (2002) Prostate tumor-stroma interaction: molecular mechanisms and opportunities for therapeutic targeting. Differentiation 70: 506–521. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

