Flock house virus RNA polymerase initiates RNA synthesis de novo and possesses a terminal nucleotidyl transferase activity
- PMID: 24466277
- PMCID: PMC3900681
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0086876
Flock house virus RNA polymerase initiates RNA synthesis de novo and possesses a terminal nucleotidyl transferase activity
Abstract
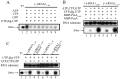
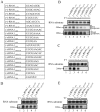
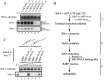
Flock House virus (FHV) is a positive-stranded RNA virus with a bipartite genome of RNAs, RNA1 and RNA2, and belongs to the family Nodaviridae. As the most extensively studied nodavirus, FHV has become a well-recognized model for studying various aspects of RNA virology, particularly viral RNA replication and antiviral innate immunity. FHV RNA1 encodes protein A, which is an RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRP) and functions as the sole viral replicase protein responsible for RNA replication. Although the RNA replication of FHV has been studied in considerable detail, the mechanism employed by FHV protein A to initiate RNA synthesis has not been determined. In this study, we characterized the RdRP activity of FHV protein A in detail and revealed that it can initiate RNA synthesis via a de novo (primer-independent) mechanism. Moreover, we found that FHV protein A also possesses a terminal nucleotidyl transferase (TNTase) activity, which was able to restore the nucleotide loss at the 3'-end initiation site of RNA template to rescue RNA synthesis initiation in vitro, and may function as a rescue and protection mechanism to protect the 3' initiation site, and ensure the efficiency and accuracy of viral RNA synthesis. Altogether, our study establishes the de novo initiation mechanism of RdRP and the terminal rescue mechanism of TNTase for FHV protein A, and represents an important advance toward understanding FHV RNA replication.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

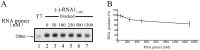


Similar articles
-
Protein Nucleotidylylation in +ssRNA Viruses.Viruses. 2021 Aug 5;13(8):1549. doi: 10.3390/v13081549. Viruses. 2021. PMID: 34452414 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Characterization of a nodavirus replicase revealed a de novo initiation mechanism of RNA synthesis and terminal nucleotidyltransferase activity.J Biol Chem. 2013 Oct 25;288(43):30785-801. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.492728. Epub 2013 Sep 9. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 24019510 Free PMC article.
-
Nodavirus-induced membrane rearrangement in replication complex assembly requires replicase protein a, RNA templates, and polymerase activity.J Virol. 2010 Dec;84(24):12492-503. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01495-10. Epub 2010 Oct 13. J Virol. 2010. PMID: 20943974 Free PMC article.
-
Flock House Virus RNA1 with a Long Heterologous Sequence at the 3'-end Can Replicate in Mammalian Cells and Mediate Reporter Gene Expression.J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2019 Nov 28;29(11):1790-1798. doi: 10.4014/jmb.1906.06054. J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2019. PMID: 31546296
-
Recent insights into the biology and biomedical applications of Flock House virus.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2008 Sep;65(17):2675-87. doi: 10.1007/s00018-008-8037-y. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2008. PMID: 18516498 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Role of Mitochondrial Membrane Spherules in Flock House Virus Replication.J Virol. 2016 Jan 20;90(7):3676-83. doi: 10.1128/JVI.03080-15. J Virol. 2016. PMID: 26792749 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and Characterization of a Human Coronavirus 229E Nonstructural Protein 8-Associated RNA 3'-Terminal Adenylyltransferase Activity.J Virol. 2019 May 29;93(12):e00291-19. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00291-19. Print 2019 Jun 15. J Virol. 2019. PMID: 30918070 Free PMC article.
-
An extensive survey of phytoviral RNA 3' uridylation identifies extreme variations and virus-specific patterns.Plant Physiol. 2023 Aug 31;193(1):271-290. doi: 10.1093/plphys/kiad278. Plant Physiol. 2023. PMID: 37177985 Free PMC article.
-
Protein Nucleotidylylation in +ssRNA Viruses.Viruses. 2021 Aug 5;13(8):1549. doi: 10.3390/v13081549. Viruses. 2021. PMID: 34452414 Free PMC article. Review.
-
In vitro particle-associated uridyltransferase activity of the rotavirus VP1 polymerase.Virology. 2022 Dec;577:24-31. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2022.09.015. Epub 2022 Oct 11. Virology. 2022. PMID: 36257129 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cai D, Qiu Y, Qi N, Yan R, Lin M, et al. (2010) Characterization of Wuhan Nodavirus subgenomic RNA3 and the RNAi inhibition property of its encoded protein B2. Virus Res 151: 153–161. - PubMed
-
- Li H, Li WX, Ding SW (2002) Induction and suppression of RNA silencing by an animal virus. Science 296: 1319–1321. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

