Regulation of amyloid precursor protein processing by serotonin signaling
- PMID: 24466315
- PMCID: PMC3897773
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0087014
Regulation of amyloid precursor protein processing by serotonin signaling
Abstract
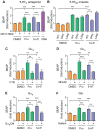
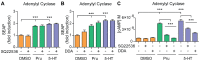
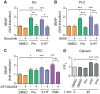
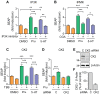
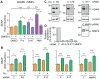
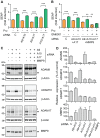
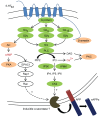
Proteolytic processing of the amyloid precursor protein (APP) by the β- and γ-secretases releases the amyloid-β peptide (Aβ), which deposits in senile plaques and contributes to the etiology of Alzheimer's disease (AD). The α-secretase cleaves APP in the Aβ peptide sequence to generate soluble APPα (sAPPα). Upregulation of α-secretase activity through the 5-hydroxytryptamine 4 (5-HT4) receptor has been shown to reduce Aβ production, amyloid plaque load and to improve cognitive impairment in transgenic mouse models of AD. Consequently, activation of 5-HT4 receptors following agonist stimulation is considered to be a therapeutic strategy for AD treatment; however, the signaling cascade involved in 5-HT4 receptor-stimulated proteolysis of APP remains to be determined. Here we used chemical and siRNA inhibition to identify the proteins which mediate 5-HT4d receptor-stimulated α-secretase activity in the SH-SY5Y human neuronal cell line. We show that G protein and Src dependent activation of phospholipase C are required for α-secretase activity, while, unexpectedly, adenylyl cyclase and cAMP are not involved. Further elucidation of the signaling pathway indicates that inositol triphosphate phosphorylation and casein kinase 2 activation is also a prerequisite for α-secretase activity. Our findings provide a novel route to explore the treatment of AD through 5-HT4 receptor-induced α-secretase activation.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- De Strooper B (2010) Proteases and proteolysis in Alzheimer disease: a multifactorial view on the disease process. Physiol Rev 90: 465–494. - PubMed
-
- Bockaert J, Claeysen S, Compan V, Dumuis A (2008) 5-HT(4) receptors: history, molecular pharmacology and brain functions. Neuropharmacology 55: 922–931. - PubMed
-
- Spencer JP, Brown JT, Richardson JC, Medhurst AD, Sehmi SS, et al. (2004) Modulation of hippocampal excitability by 5-HT4 receptor agonists persists in a transgenic model of Alzheimer's disease. Neuroscience 129: 49–54. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

