Effects of tyrosine kinase inhibitors and CXCR4 antagonist on tumor growth and angiogenesis in rat glioma model: MRI and protein analysis study
- PMID: 24466368
- PMCID: PMC3890700
- DOI: 10.1593/tlo.13559
Effects of tyrosine kinase inhibitors and CXCR4 antagonist on tumor growth and angiogenesis in rat glioma model: MRI and protein analysis study
Abstract
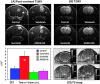
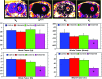
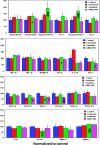
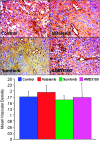
The aim of the study was to determine the antiangiogenic efficacy of vatalanib, sunitinib, and AMD3100 in an animal model of human glioblastoma (GBM) by using dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging (DCE-MRI) and tumor protein expression analysis. Orthotopic GBM-bearing animals were randomly assigned either to control group or vatalanib, sunitinib, and AMD3100 treatment groups. Following 2 weeks of drug treatment, tumor growth and vascular parameters were measured using DCE-MRI. Expression of different angiogenic factors in tumor extracts was measured using a membrane-based human antibody array kit. Tumor angiogenesis and invasion were determined by immunohistochemistry. DCE-MRI showed a significant increase in tumor size after vatalanib treatment. AMD3100-treated group showed a significant decrease in a number of vascular parameters determined by DCE-MRI. AMD3100 significantly decreased the expression of different angiogenic factors compared to sunitinib or vatalanib; however, there were no significant changes in vascular density among the groups. Sunitinib-treated animals showed significantly higher migration of the invasive cells, whereas in both vatalanib- and AMD3100-treated animals the invasive cell migration distance was significantly lower compared to that of control. Vatalanib and sunitinib resulted in suboptimal therapeutic effect, but AMD3100 treatment resulted in a significant reduction in tumor growth, permeability, interstitial space volume, and invasion of tumor cells in an animal model of GBM.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Combination of vatalanib and a 20-HETE synthesis inhibitor results in decreased tumor growth in an animal model of human glioma.Onco Targets Ther. 2016 Mar 9;9:1205-19. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S93790. eCollection 2016. Onco Targets Ther. 2016. PMID: 27022280 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting Bone Marrow to Potentiate the Anti-Tumor Effect of Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor in Preclinical Rat Model of Human Glioblastoma.Int J Cancer Res. 2016;12(2):69-81. doi: 10.3923/ijcr.2016.69.81. Epub 2016 Mar 15. Int J Cancer Res. 2016. PMID: 27429653 Free PMC article.
-
MRI biomarkers identify the differential response of glioblastoma multiforme to anti-angiogenic therapy.Neuro Oncol. 2014 Jun;16(6):868-79. doi: 10.1093/neuonc/nou040. Epub 2014 Apr 23. Neuro Oncol. 2014. PMID: 24759636 Free PMC article.
-
Imaging biomarkers guided anti-angiogenic therapy for malignant gliomas.Neuroimage Clin. 2018 Jul 5;20:51-60. doi: 10.1016/j.nicl.2018.07.001. eCollection 2018. Neuroimage Clin. 2018. PMID: 30069427 Free PMC article. Review.
-
DCE-MRI in hepatocellular carcinoma-clinical and therapeutic image biomarker.World J Gastroenterol. 2014 Mar 28;20(12):3125-34. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i12.3125. World J Gastroenterol. 2014. PMID: 24695624 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Targeting Glioma with a Dual Mode Optical and Paramagnetic Nanoprobe across the Blood-brain Tumor Barrier.J Nanomed Nanotechnol. 2016 Aug;7(4):395. doi: 10.4172/2157-7439.1000395. Epub 2016 Aug 31. J Nanomed Nanotechnol. 2016. PMID: 27695645 Free PMC article.
-
Vascular mimicry: changing the therapeutic paradigms in cancer.Mol Biol Rep. 2020 Jun;47(6):4749-4765. doi: 10.1007/s11033-020-05515-2. Epub 2020 May 18. Mol Biol Rep. 2020. PMID: 32424524 Review.
-
G protein-coupled receptors as oncogenic signals in glioma: emerging therapeutic avenues.Neuroscience. 2014 Oct 10;278:222-36. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2014.08.015. Epub 2014 Aug 24. Neuroscience. 2014. PMID: 25158675 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Combination of vatalanib and a 20-HETE synthesis inhibitor results in decreased tumor growth in an animal model of human glioma.Onco Targets Ther. 2016 Mar 9;9:1205-19. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S93790. eCollection 2016. Onco Targets Ther. 2016. PMID: 27022280 Free PMC article.
-
Vascular Mimicry: The Next Big Glioblastoma Target.Biochem Physiol. 2015 Sep;4(3):e410. doi: 10.4172/2168-9652.1000e140. Epub 2015 Aug 31. Biochem Physiol. 2015. PMID: 27042399 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Los M, Roodhart JM, Voest EE. Target practice: lessons from phase III trials with bevacizumab and vatalanib in the treatment of advanced colorectal cancer. Oncologist. 2007;12:443–450. - PubMed
-
- Norden AD, Young GS, Setayesh K, Muzikansky A, Klufas R, Ross GL, Ciampa AS, Ebbeling LG, Levy B, Drappatz J, et al. Bevacizumab for recurrent malignant gliomas: efficacy, toxicity, and patterns of recurrence. Neurology. 2008;70:779–787. - PubMed
-
- Norden AD, Drappatz J, Wen PY. Novel anti-angiogenic therapies for malignant gliomas. Lancet Neurol. 2008;7:1152–1160. - PubMed
-
- Dietrich J, Norden AD, Wen PY. Emerging antiangiogenic treatments for gliomas—efficacy and safety issues. Curr Opin Neurol. 2008;21:736–744. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
