Correlation of MicroRNA 132 Up-regulation with an Unfavorable Clinical Outcome in Patients with Primary Glioblastoma Multiforme Treated with Radiotherapy Plus Concomitant and Adjuvant Temozolomide Chemotherapy
- PMID: 24466377
- PMCID: PMC3890709
- DOI: 10.1593/tlo.13553
Correlation of MicroRNA 132 Up-regulation with an Unfavorable Clinical Outcome in Patients with Primary Glioblastoma Multiforme Treated with Radiotherapy Plus Concomitant and Adjuvant Temozolomide Chemotherapy
Abstract
Background: MicroRNA 132 (miR-132) is dysregulated in a range of human malignancies; however, its role in glioma has not been reported. The aim of this study was to profile miR-132 expression in a cohort of patients with primary glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) treated with the Stupp regimen and to correlate microRNA levels with patient outcome.
Methods: miR-132 levels relative to RNU44 were assessed by quantitative reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction in 43 GBMs and normal brain tissue. The cohort comprised patients less than 72 years of age with Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group (ECOG) scores between 0 and 2 who had undergone 6-week concomitant radiation and temozolomide followed by adjuvant temozolomide. Survival data were available for all cases. Tumors were characterized for O6-methylguanine-DNA methyltransferase (MGMT) methylation and isocitrate dehydrogenase (IDH) 1/2 mutation status. Associations between miR-132 expression and clinical indicators were analyzed.
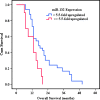
Results: Tumor miR-132 levels ranged from 0.07- to 40.4-fold increase (mean = 5.5-fold increase) relative to normal brain. High-level miR-132 (above the mean) independently predicted for a significantly shorter overall survival (P = .008). miR-132 was a stronger prognostic indicator than ECOG score (P = .012) and age at diagnosis (P = .026) but did not correlate with MGMT methylation status or extent of tumor resection. Cox regression analysis confirmed high miR-132 as the strongest predictor of outcome (P = .010) with a hazard ratio of 2.8.
Conclusions: This study identified high miR-132 expression as a biomarker of poor prognosis in patients with primary GBM treated with the Stupp regimen.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Immunohistochemical analysis of O6-methylguanine-DNA methyltransferase (MGMT) protein expression as prognostic marker in glioblastoma patients treated with radiation therapy with concomitant and adjuvant Temozolomide.J Egypt Natl Canc Inst. 2016 Mar;28(1):23-30. doi: 10.1016/j.jnci.2015.11.003. Epub 2015 Dec 10. J Egypt Natl Canc Inst. 2016. PMID: 26682634
-
Is the absolute value of O(6)-methylguanine-DNA methyltransferase gene messenger RNA a prognostic factor, and does it predict the results of treatment of glioblastoma with temozolomide?J Neurosurg. 2014 Oct;121(4):818-26. doi: 10.3171/2014.6.JNS132535. Epub 2014 Aug 8. J Neurosurg. 2014. PMID: 25105699
-
O(6) -methylguanine-DNA methyltransferase (MGMT) promoter methylation and low MGMT-encoded protein expression as prognostic markers in glioblastoma patients treated with biodegradable carmustine wafer implants after initial surgery followed by radiotherapy with concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide.Cancer. 2012 Sep 15;118(18):4545-54. doi: 10.1002/cncr.27441. Epub 2012 Feb 22. Cancer. 2012. PMID: 22359215
-
Prognostic significance of O6-methylguanine-DNA-methyltransferase (MGMT) promoter methylation and isocitrate dehydrogenase-1 (IDH-1) mutation in glioblastoma multiforme patients: A single-center experience in the Middle East region.Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2019 Jul;182:92-97. doi: 10.1016/j.clineuro.2019.04.008. Epub 2019 Apr 29. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2019. PMID: 31108342
-
Glioblastoma Multiforme and Genetic Mutations: The Issue Is Not Over Yet. An Overview of the Current Literature.J Neurol Surg A Cent Eur Neurosurg. 2020 Jan;81(1):64-70. doi: 10.1055/s-0039-1688911. Epub 2019 Sep 24. J Neurol Surg A Cent Eur Neurosurg. 2020. PMID: 31550738 Review.
Cited by
-
Machine learning and bioinformatics approaches for classification and clinical detection of bevacizumab responsive glioblastoma subtypes based on miRNA expression.Sci Rep. 2022 May 23;12(1):8685. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-12566-x. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35606527 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of expression of O6-methylguanine-DNA methyltransferase and the treatment of glioblastoma (Review).Int J Oncol. 2015 Aug;47(2):417-28. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2015.3026. Epub 2015 May 29. Int J Oncol. 2015. PMID: 26035292 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MicroRNA as potential biomarkers in Glioblastoma.J Neurooncol. 2015 Nov;125(2):237-48. doi: 10.1007/s11060-015-1912-0. Epub 2015 Sep 21. J Neurooncol. 2015. PMID: 26391593 Review.
-
High-throughput microRNA profile in adult and pediatric primary glioblastomas: the role of miR-10b-5p and miR-630 in the tumor aggressiveness.Mol Biol Rep. 2020 Sep;47(9):6949-6959. doi: 10.1007/s11033-020-05754-3. Epub 2020 Sep 4. Mol Biol Rep. 2020. PMID: 32888124
-
Mitochondria Transcription Factor A: A Putative Target for the Effect of Melatonin on U87MG Malignant Glioma Cell Line.Molecules. 2018 May 9;23(5):1129. doi: 10.3390/molecules23051129. Molecules. 2018. PMID: 29747444 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Stupp R, Mason WP, van den Bent MJ, Weller M, Fisher B, Taphoorn MJ, Belanger K, Brandes AA, Marosi C, Bogdahn U, et al. Radiotherapy plus concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide for glioblastoma. N Engl J Med. 2005;352:987–996. - PubMed
-
- Stupp R, Hegi ME, Mason WP, van den Bent MJ, Taphoorn MJ, Janzer RC, Ludwin SK, Allgeier A, Fisher B, Belanger K, et al. Effects of radiotherapy with concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide versus radiotherapy alone on survival in glioblastoma in a randomised phase III study: 5-year analysis of the EORTC-NCIC trial. Lancet Oncol. 2009;10:459–466. - PubMed
-
- Ambros V. The functions of animal microRNAs. Nature. 2004;431:350–355. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
