Randomized, sham controlled trial of transcranial direct current stimulation for painful diabetic polyneuropathy
- PMID: 24466511
- PMCID: PMC3895516
- DOI: 10.5535/arm.2013.37.6.766
Randomized, sham controlled trial of transcranial direct current stimulation for painful diabetic polyneuropathy
Abstract
Objective: To investigate the analgesic effect of transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS) over the primary motor (M1), dorsolateral prefrontal cortex (DLPFC), and sham tDCS in patients with painful diabetic polyneuropathy (PDPN).
Methods: Patients with PDPN (n=60) were divided randomly into the three groups (n=20 per group). Each group received anodal tDCS with the anode centered over the left M1, DLPFC, or sham stimulation for 20 minutes at intensity of 2 mA for 5 consecutive days. A blinded physician rated the patients' pain using a visual analog scale (VAS), Clinical Global Impression (CGI) score, anxiety score, sleep quality, Beck Depression Inventory (BDI), and the pain threshold (PT) to pressure.
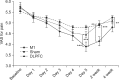
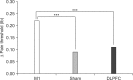
Results: After the tDCS sessions, the M1 group showed a significantly greater reduction in VAS for pain and PT versus the sham and DLPFC groups (p<0.001). The reduction in VAS for pain was sustained after 2 and 4 weeks of follow-up in the M1 group compared with the sham group (p<0.001, p=0.007). Significant differences were observed among the three groups over time in VAS for pain (p<0.001), CGI score (p=0.01), and PT (p<0.001). No significant difference was observed among the groups in sleep quality, anxiety score, or BDI score immediately after tDCS.
Conclusion: Five daily sessions of tDCS over the M1 can produce immediate pain relief, and relief 2- and 4-week in duration in patients with PDPN. Our findings provide the first evidence of a beneficial effect of tDCS on PDPN.
Keywords: Chronic pain; Diabetic neuropathy; Transcranial direct current stimulation.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures



References
-
- Boulton AJ, Malik RA, Arezzo JC, Sosenko JM. Diabetic somatic neuropathies. Diabetes Care. 2004;27:1458–1486. - PubMed
-
- Davies M, Brophy S, Williams R, Taylor A. The prevalence, severity, and impact of painful diabetic peripheral neuropathy in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2006;29:1518–1522. - PubMed
-
- Jensen MP, Chodroff MJ, Dworkin RH. The impact of neuropathic pain on health-related quality of life: review and implications. Neurology. 2007;68:1178–1182. - PubMed
-
- Tesfaye S, Chaturvedi N, Eaton SE, Ward JD, Manes C, Ionescu-Tirgoviste C, et al. Vascular risk factors and diabetic neuropathy. N Engl J Med. 2005;352:341–350. - PubMed
-
- Baron R. Mechanisms of disease: neuropathic pain: a clinical perspective. Nat Clin Pract Neurol. 2006;2:95–106. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

