Integrin cytoplasmic tail interactions
- PMID: 24467163
- PMCID: PMC3985435
- DOI: 10.1021/bi401596q
Integrin cytoplasmic tail interactions
Abstract
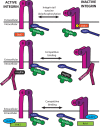
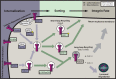
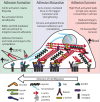
Integrins are heterodimeric cell surface adhesion receptors essential for multicellular life. They connect cells to the extracellular environment and transduce chemical and mechanical signals to and from the cell. Intracellular proteins that bind the integrin cytoplasmic tail regulate integrin engagement of extracellular ligands as well as integrin localization and trafficking. Cytoplasmic integrin-binding proteins also function downstream of integrins, mediating links to the cytoskeleton and to signaling cascades that impact cell motility, growth, and survival. Here, we review key integrin-interacting proteins and their roles in regulating integrin activity, localization, and signaling.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

