Presence of Epstein-Barr virus-infected B lymphocytes with thyrotropin receptor antibodies on their surface in Graves' disease patients and in healthy individuals
- PMID: 24467196
- PMCID: PMC5351790
- DOI: 10.3109/08916934.2013.879863
Presence of Epstein-Barr virus-infected B lymphocytes with thyrotropin receptor antibodies on their surface in Graves' disease patients and in healthy individuals
Erratum in
-
Erratum.Autoimmunity. 2015;48(7):502. doi: 10.3109/08916934.2015.1052245. Epub 2015 May 27. Autoimmunity. 2015. PMID: 26017700 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Graves' disease is an autoimmune hyperthyroidism caused by thyrotropin receptor antibodies (TRAbs). Because Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) persists in B cells and is occasionally reactivated, we hypothesized that EBV contributes to TRAbs production in Graves' disease patients by stimulating the TRAbs-producing B cells. In order for EBV to stimulate antibody-producing cells, EBV must be present in those cells but that have not yet been observed. We examined whether EBV-infected (EBV(+)) B cells with TRAbs on their surface (TRAbs(+)) as membrane immunoglobulin were present in peripheral blood of Graves' disease patients. We analyzed cultured or non-cultured peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) from 13 patients and 11 healthy controls by flow-cytometry and confocal laser microscopy, and confirmed all cultured PBMCs from 8 patients really had TRAbs(+) EBV(+) double positive cells. We unexpectedly detected TRAbs(+) cells in all healthy controls, and TRAbs(+) EBV(+) double positive cells in all cultured PBMC from eight healthy controls. The frequency of TRAbs(+) cells in cultured PBMCs was significantly higher in patients than in controls (p = 0.021). In this study, we indicated the presence of EBV-infected B lymphocytes with TRAbs on their surface, a possible player of the production of excessive TRAbs, the causative autoantibody for Graves' disease. This is a basic evidence for our hypothesis that EBV contributes to TRAbs production in Graves' disease patients. Our results further suggest that healthy controls have the potential for TRAbs production. This gives us an important insight into the pathogenesis of Graves' disease.
Figures
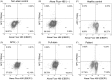


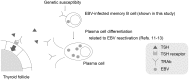
Similar articles
-
Reactivation of persistent Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) causes secretion of thyrotropin receptor antibodies (TRAbs) in EBV-infected B lymphocytes with TRAbs on their surface.Autoimmunity. 2015;48(5):328-35. doi: 10.3109/08916934.2015.1022163. Epub 2015 Mar 11. Autoimmunity. 2015. PMID: 25759125
-
Subclinical Epstein-Barr Virus Primary Infection and Lytic Reactivation Induce Thyrotropin Receptor Autoantibodies.Viral Immunol. 2019 Nov;32(9):362-369. doi: 10.1089/vim.2019.0086. Epub 2019 Oct 3. Viral Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31580214 Free PMC article.
-
Epstein-Barr virus reactivation in peripheral B lymphocytes induces IgM-type thyrotropin receptor autoantibody production in patients with Graves' disease.Endocr J. 2023 Jun 28;70(6):619-627. doi: 10.1507/endocrj.EJ22-0609. Epub 2023 Mar 10. Endocr J. 2023. PMID: 36908137
-
TSH-receptor autoantibodies: pathophysiology, assay methods, and clinical applications.Minerva Endocrinol. 2018 Sep;43(3):323-332. doi: 10.23736/S0391-1977.17.02791-2. Epub 2017 Dec 21. Minerva Endocrinol. 2018. PMID: 29265783 Review.
-
Functional diagnostics for thyrotropin hormone receptor autoantibodies: bioassays prevail over binding assays.Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2018 Jun 1;23(11):2028-2043. doi: 10.2741/4687. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2018. PMID: 29772543 Review.
Cited by
-
Thyrotropin Receptor Antibody (TRAb)-IgM Levels Are Markedly Higher Than TRAb-IgG Levels in Graves' Disease Patients and Controls, and TRAb-IgM Production Is Related to Epstein-Barr Virus Reactivation.Viral Immunol. 2016 Oct;29(8):459-463. doi: 10.1089/vim.2016.0043. Epub 2016 Aug 16. Viral Immunol. 2016. PMID: 27529807 Free PMC article.
-
High Level Estradiol Induces EBV Reactivation and EBV gp350/220(+)CD138(+) Double-positive B Cell Population in Graves' Disease Patients and Healthy Controls.Yonago Acta Med. 2019 Jun 20;62(2):240-243. doi: 10.33160/yam.2019.06.010. eCollection 2019 Jun. Yonago Acta Med. 2019. PMID: 31341401 Free PMC article.
-
Production of thyrotropin receptor antibodies in acute phase of infectious mononucleosis due to Epstein-Barr virus primary infection: a case report of a child.Springerplus. 2015 Aug 27;4:456. doi: 10.1186/s40064-015-1236-8. eCollection 2015. Springerplus. 2015. PMID: 26322262 Free PMC article.
-
Epstein-Barr Virus Lytic Reactivation Induces IgG4 Production by Host B Lymphocytes in Graves' Disease Patients and Controls: A Subset of Graves' Disease Is an IgG4-Related Disease-Like Condition.Viral Immunol. 2018 Oct;31(8):540-547. doi: 10.1089/vim.2018.0042. Epub 2018 Sep 17. Viral Immunol. 2018. PMID: 30222515 Free PMC article.
-
Epstein-Barr Virus Lytic Reactivation Activates B Cells Polyclonally and Induces Activation-Induced Cytidine Deaminase Expression: A Mechanism Underlying Autoimmunity and Its Contribution to Graves' Disease.Viral Immunol. 2017 Apr;30(3):240-249. doi: 10.1089/vim.2016.0179. Epub 2017 Mar 23. Viral Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28333576 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Davies P., Larsen T. 2007. Thyrotoxicosis. In Williams Textbook of Endocrinology, 11th ed. Kronenberg H. M., Melmed S., Polonsky K. S., Larsen P. R., eds. Saunders, Philadelphia, PA: p. 333–376
-
- Weetman A. P., McGregor. A. M. 1994. Autoimmune thyroid disease: further developments in our understanding. Endocr. Rev. 15: 788–830 - PubMed
-
- Tomer Y. Greenberg A. Barbesino G. et al. 2001. CTLA-4 and not CD28 is a susceptibility gene for thyroid autoantibody production. JCEM. 86: 1687–1693 - PubMed
-
- Ueda H. Howson J. M. M. Esposito L. et al. 2003. Association of the T-cell regulatory gene CTLA4 with susceptibility to autoimmune disease. Nature. 423: 506–511 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
