Caspase-8 as a regulator of tumor cell motility
- PMID: 24467204
- PMCID: PMC4106798
- DOI: 10.2174/1566524014666140128111951
Caspase-8 as a regulator of tumor cell motility
Abstract
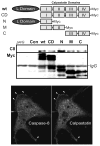
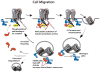
The caspases are a family of ubiquitously expressed cysteine proteases best known for their roles in programmed cell death. However, caspases play a number of other roles in vertebrates. In the case of caspase-8, loss of expression is an embryonic lethal phenotype, and caspase-8 plays roles in suppressing cellular necrosis, promoting differentiation and immune signaling, regulating autophagy, and promoting cellular migration. Apoptosis and migration require localization of caspase-8 in the periphery of the cells, where caspase-8 acts as part of distinct biosensory complexes that either promote migration in appropriate cellular microenvironments, or cell death in inappropriate settings. In the cellular periphery, caspase-8 interacts with components of the focal adhesion complex in a tyrosine-kinase dependent manner, promoting both cell migration in vitro and metastasis in vivo. Mechanistically, caspase-8 interacts with components of both focal adhesions and early endosomes, enhancing focal adhesion turnover and promoting rapid integrin recycling to the cell surface. Clinically, this suggests that the expression of caspase-8 may not always be a positive prognostic sign, and that the role of caspase-8 in cancer progression is likely context-dependent.
Figures

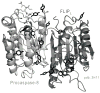

Similar articles
-
Caspase-8 association with the focal adhesion complex promotes tumor cell migration and metastasis.Cancer Res. 2009 May 1;69(9):3755-63. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-08-3937. Epub 2009 Apr 21. Cancer Res. 2009. PMID: 19383910 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of a critical tyrosine residue in caspase 8 that promotes cell migration.J Biol Chem. 2008 May 9;283(19):13031-4. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M800549200. Epub 2008 Jan 23. J Biol Chem. 2008. PMID: 18216014 Free PMC article.
-
Caspase-8 as a therapeutic target in cancer.Cancer Lett. 2013 May 28;332(2):133-40. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2010.07.022. Epub 2010 Sep 3. Cancer Lett. 2013. PMID: 20817393 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Rab5 mediates caspase-8-promoted cell motility and metastasis.Mol Biol Cell. 2010 Jan 15;21(2):369-76. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e09-09-0769. Epub 2009 Nov 18. Mol Biol Cell. 2010. PMID: 19923319 Free PMC article.
-
Caspase-8 function, and phosphorylation, in cell migration.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2018 Oct;82:105-117. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2018.01.009. Epub 2018 Feb 17. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2018. PMID: 29410361 Review.
Cited by
-
Caspase-8 knockdown suppresses apoptosis, while induces autophagy and chemo-sensitivity in non-small cell lung cancer cells.Am J Transl Res. 2020 Oct 15;12(10):6478-6489. eCollection 2020. Am J Transl Res. 2020. PMID: 33194045 Free PMC article.
-
The stressosome, a caspase-8-activating signalling complex assembled in response to cell stress in an ATG5-mediated manner.J Cell Mol Med. 2021 Sep;25(18):8809-8820. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.16840. Epub 2021 Aug 7. J Cell Mol Med. 2021. PMID: 34363313 Free PMC article.
-
Galactose:PEGamine coated gold nanoparticles adhere to filopodia and cause extrinsic apoptosis.Nanoscale Adv. 2018 Nov 12;1(2):807-816. doi: 10.1039/c8na00270c. eCollection 2019 Feb 12. Nanoscale Adv. 2018. PMID: 36132240 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of tumor microenvironment-related genes in lower-grade gliomas by mining TCGA database.Transl Cancer Res. 2020 Aug;9(8):4583-4595. doi: 10.21037/tcr-20-1079. Transl Cancer Res. 2020. PMID: 35117823 Free PMC article.
-
2-Methoxyestradiol improves the apoptosis level in keloid fibroblasts through caspase-dependent mechanisms in vitro.Am J Transl Res. 2018 Dec 15;10(12):4017-4029. eCollection 2018. Am J Transl Res. 2018. PMID: 30662647 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Teesalu T, Sugahara KN, Ruoslahti E. Mapping of vascular ZIP codes by phage display. Methods Enzymol. 2012;503:35–56. - PubMed
-
- Frisch SM, Screaton RA. Anoikis mechanisms. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2001 Oct;13(5):555–62. - PubMed
-
- Buchheit CL, Rayavarapu RR, Schafer ZT. The regulation of cancer cell death and metabolism by extracellular matrix attachment. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2012 Jun;23(4):402–11. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
