Metabolic syndrome and cardiovascular risk among long-term survivors of acute lymphoblastic leukaemia - From the St. Jude Lifetime Cohort
- PMID: 24467690
- PMCID: PMC4271734
- DOI: 10.1111/bjh.12754
Metabolic syndrome and cardiovascular risk among long-term survivors of acute lymphoblastic leukaemia - From the St. Jude Lifetime Cohort
Abstract
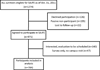
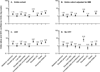
Adult survivors of childhood acute lymphoblastic leukaemia (ALL) have a four-fold excess risk of mortality from cardiovascular disease. This cardiovascular risk has not been fully characterized. ALL survivors [n = 784, median age 31·7 years (18·9-59·1)] in the St. Jude Lifetime Cohort Study underwent evaluation for cardiovascular risk and metabolic syndrome (MetS) according to National Cholesterol Education Program - Adult Treatment Panel III criteria. Comparisons were made to 777 age-, sex-, and race-matched controls from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES). MetS was identified in 259 survivors (33·6%) and associated with older age in 5-year increments (relative risk [RR] 1·13, 95% confidence interval [CI] 1·06-1·19) and prior cranial radiotherapy (CRT) (with craniospinal radiation: RR 1·88, 95%CI 1·32-2·67; without: RR 1·67, 95%CI 1·26-2·23). Measures of obesity were highly prevalent among female survivors and CRT recipients. Compared to NHANES controls, ALL survivors had a higher risk of MetS (RR 1·43, 95%CI 1·22-1·69), hypertension (RR 2·43, 95%CI 2·06-2·86), low high-density lipoprotein (RR 1·40, 95%CI 1·23-1·59), obesity (RR 1·47, 95%CI 1·29-1·68) and insulin resistance (1·64, 95%CI 1·44-1·86). This large study of clinically evaluated ALL survivors identified a high prevalence of MetS, obesity and cardiovascular risk, particularly in CRT recipients, underscoring the need for screening and aggressive reduction of modifiable risks.
Keywords: acute lymphoblastic leukaemia; cardiovascular risk; childhood cancer survivors; cranial radiotherapy; metabolic syndrome.
© 2014 John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
References
-
- Allen A. The cardiotoxicity of chemotherapeutic drugs. Semin Oncol. 1992;19:529–542. - PubMed
-
- Armstrong GT, Oeffinger KC, Chen Y, Kawashima T, Yasui Y, Leisenring W, Stovall M, Chow EJ, Sklar CA, Mulrooney DA, Mertens AC, Border W, Durand JB, Robison LL, Meacham LR. Modifiable Risk Factors and Major Cardiac Events Among Adult Survivors of Childhood Cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2013;31:3673–3680. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Beauloye V, Steffens M, Zech F, Vermylen C, Maiter D. Characterization of insulin resistance in young adult survivors of childhood acute lymphoblastic leukaemia and non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 2012 - PubMed
-
- Chen J, Wildman RP, Hamm LL, Muntner P, Reynolds K, Whelton PK, He J. Association between inflammation and insulin resistance in U.S. nondiabetic adults: results from the Third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Diabetes Care. 2004;27:2960–2965. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

