Changes in cerebral oxygenation during early postnatal adaptation in newborns delivered by vacuum extraction measured by near-infrared spectroscopy
- PMID: 24467703
- PMCID: PMC3913969
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2431-14-21
Changes in cerebral oxygenation during early postnatal adaptation in newborns delivered by vacuum extraction measured by near-infrared spectroscopy
Abstract
Background: Newborns delivered by vacuum extraction quite often show clinical signs of a hemodynamic compromise, which is difficult to assess in terms of severity. The conventional means to measure the hemodynamic status are not sensitive enough to appreciate the severity of general, and more specifically of cerebral circulatory imbalance. The aim was to study cerebral tissue oxygenation during postnatal adaptation in these infants using near-infrared spectroscopy.
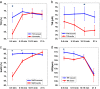
Methods: The tissue hemoglobin index (THI), tissue oxygenation index (TOI), arterial oxygen saturation (pre-ductal SaO₂) and heart rate (HR) were recorded immediately after birth, and again after 12-24 hours of life in 15 newborns delivered by vacuum extraction due to fetal distress. A comparison with 19 healthy newborns delivered by elective cesarean section was performed.
Results: Newborns delivered by vacuum extraction had significantly higher THI 10 to 15 minutes after birth. TOI and HR were significantly higher in the first 5 min and SaO₂ in the first 10 minutes but then did not differ from those after cesarean section.
Conclusion: Infants delivered by vacuum extraction following fetal distress show transient deviations in cerebral oxygenation and perfusion after birth which were not detectable after 24 hours.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Near-infrared spectroscopy measurements of cerebral oxygenation in newborns during immediate postnatal adaptation.J Pediatr. 2010 Mar;156(3):372-6. doi: 10.1016/j.jpeds.2009.09.050. Epub 2009 Nov 14. J Pediatr. 2010. PMID: 19914638
-
Near-infrared spectroscopic cerebral oxygenation reading in neonates and infants is associated with central venous oxygen saturation.Paediatr Anaesth. 2005 Feb;15(2):102-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9592.2005.01404.x. Paediatr Anaesth. 2005. PMID: 15675925
-
Reference ranges for regional cerebral tissue oxygen saturation and fractional oxygen extraction in neonates during immediate transition after birth.J Pediatr. 2013 Dec;163(6):1558-63. doi: 10.1016/j.jpeds.2013.07.007. Epub 2013 Aug 22. J Pediatr. 2013. PMID: 23972642
-
Monitoring regional tissue oxygen extraction in neonates <1250 g helps identify transfusion thresholds independent of hematocrit.J Neonatal Perinatal Med. 2014 Jan 1;7(2):89-100. doi: 10.3233/NPM-1477213. J Neonatal Perinatal Med. 2014. PMID: 25104129 Review.
-
Monitoring neonatal regional cerebral oxygen saturation in clinical practice: value and pitfalls.Neonatology. 2008;94(4):237-44. doi: 10.1159/000151642. Epub 2008 Sep 11. Neonatology. 2008. PMID: 18784420 Review.
Cited by
-
Cerebral Tissue Oxygenation during Immediate Neonatal Transition and Resuscitation.Front Pediatr. 2017 Feb 23;5:29. doi: 10.3389/fped.2017.00029. eCollection 2017. Front Pediatr. 2017. PMID: 28280719 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of cerebral oxygenation for prediction of hypotension after spinal anesthesia for caesarean section.J Clin Monit Comput. 2016 Aug;30(4):417-21. doi: 10.1007/s10877-015-9733-4. Epub 2015 Jul 18. J Clin Monit Comput. 2016. PMID: 26186992
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources