Sertolin mediates blood-testis barrier restructuring
- PMID: 24467744
- PMCID: PMC3959606
- DOI: 10.1210/en.2013-1850
Sertolin mediates blood-testis barrier restructuring
Abstract
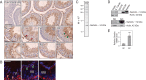
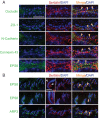
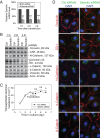
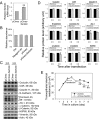
Two important events that occur during mammalian spermatogenesis are the release of elongated spermatids at late stage VIII of the seminiferous epithelial cycle and the restructuring of the blood-testis barrier (BTB) during stages VIII-XI. Still, it is not completely understood how these cellular events are accomplished within the seminiferous epithelium. In the present study, we investigate how sertolin, a protein that was initially identified, cloned, and partially characterized by our laboratory, functions in these critical events. Sertolin was found at the BTB, as well as at the apical ectoplasmic specialization and apical tubulobulbar complex, where it colocalized with epidermal growth factor receptor kinase substrate 8 and actin-related protein 3, two actin-regulatory proteins. Knockdown of sertolin by RNA interference showed Sertoli cell barrier function to be enhanced when assessed by transepithelial electrical resistance measurements and immunolocalization experiments. By contrast, the integrity of the BTB was disrupted when sertolin was overexpressed in vitro and in vivo. Sertolin overexpression also prompted germ cell loss from the seminiferous epithelium. Taken collectively, these results suggest that sertolin may be involved in coordinating spermatid release and BTB restructuring during spermatogenesis in the rat.
Figures
References
-
- de Kretser DM, Kerr JB. The cytology of the testis. In: Knobil E, Neill JB, Ewing LL, Greenwald GS, Markert CL, Pfaff DW, eds. The Physiology of Reproduction. New York, NY: Raven Press; 1988:837–932
-
- Handel MA, Schimenti JC. Genetics of mammalian meiosis: regulation, dynamics and impact on fertility. Nat Rev Genet. 2010;11:124–136 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

