Production of a reference transcriptome and transcriptomic database (EdwardsiellaBase) for the lined sea anemone, Edwardsiella lineata, a parasitic cnidarian
- PMID: 24467778
- PMCID: PMC3909931
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2164-15-71
Production of a reference transcriptome and transcriptomic database (EdwardsiellaBase) for the lined sea anemone, Edwardsiella lineata, a parasitic cnidarian
Abstract
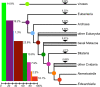
Background: The lined sea anemone Edwardsiella lineata is an informative model system for evolutionary-developmental studies of parasitism. In this species, it is possible to compare alternate developmental pathways leading from a larva to either a free-living polyp or a vermiform parasite that inhabits the mesoglea of a ctenophore host. Additionally, E. lineata is confamilial with the model cnidarian Nematostella vectensis, providing an opportunity for comparative genomic, molecular and organismal studies.
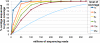
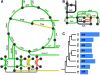
Description: We generated a reference transcriptome for E. lineata via high-throughput sequencing of RNA isolated from five developmental stages (parasite; parasite-to-larva transition; larva; larva-to-adult transition; adult). The transcriptome comprises 90,440 contigs assembled from >15 billion nucleotides of DNA sequence. Using a molecular clock approach, we estimated the divergence between E. lineata and N. vectensis at 215-364 million years ago. Based on gene ontology and metabolic pathway analyses and gene family surveys (bHLH-PAS, deiodinases, Fox genes, LIM homeodomains, minicollagens, nuclear receptors, Sox genes, and Wnts), the transcriptome of E. lineata is comparable in depth and completeness to N. vectensis. Analyses of protein motifs and revealed extensive conservation between the proteins of these two edwardsiid anemones, although we show the NF-κB protein of E. lineata reflects the ancestral structure, while the NF-κB protein of N. vectensis has undergone a split that separates the DNA-binding domain from the inhibitory domain. All contigs have been deposited in a public database (EdwardsiellaBase), where they may be searched according to contig ID, gene ontology, protein family motif (Pfam), enzyme commission number, and BLAST. The alignment of the raw reads to the contigs can also be visualized via JBrowse.
Conclusions: The transcriptomic data and database described here provide a platform for studying the evolutionary developmental genomics of a derived parasitic life cycle. In addition, these data from E. lineata will aid in the interpretation of evolutionary novelties in gene sequence or structure that have been reported for the model cnidarian N. vectensis (e.g., the split NF-κB locus). Finally, we include custom computational tools to facilitate the annotation of a transcriptome based on high-throughput sequencing data obtained from a "non-model system."
Figures








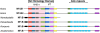

Similar articles
-
Comparative anatomy and histology of developmental and parasitic stages in the life cycle of the lined sea anemone Edwardsiella lineata.J Parasitol. 2009 Feb;95(1):100-12. doi: 10.1645/GE-1623.1. J Parasitol. 2009. PMID: 18656992
-
TEMPERATURE AND SALINITY AFFECT DEVELOPMENT OF THE PARASITIC SEA ANEMONE EDWARDSIELLA LINEATA POTENTIALLY LIMITING ITS IMPACT AS A BIOLOGICAL CONTROL ON THE CTENOPHORE MNEMIOPSIS LEIDYI.J Parasitol. 2023 Dec 1;109(6):574-579. doi: 10.1645/23-15. J Parasitol. 2023. PMID: 38104628
-
Ecological and developmental dynamics of a host-parasite system involving a sea anemone and two ctenophores.J Parasitol. 2007 Dec;93(6):1392-402. doi: 10.1645/GE-1250.1. J Parasitol. 2007. PMID: 18314686
-
Environmental sensing and response genes in cnidaria: the chemical defensome in the sea anemone Nematostella vectensis.Cell Biol Toxicol. 2008 Dec;24(6):483-502. doi: 10.1007/s10565-008-9107-5. Epub 2008 Oct 28. Cell Biol Toxicol. 2008. PMID: 18956243 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Rising starlet: the starlet sea anemone, Nematostella vectensis.Bioessays. 2005 Feb;27(2):211-21. doi: 10.1002/bies.20181. Bioessays. 2005. PMID: 15666346 Review.
Cited by
-
Global Neuropeptide Annotations From the Genomes and Transcriptomes of Cubozoa, Scyphozoa, Staurozoa (Cnidaria: Medusozoa), and Octocorallia (Cnidaria: Anthozoa).Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2019 Dec 6;10:831. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2019.00831. eCollection 2019. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2019. PMID: 31866941 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptome of Sphaerospora molnari (Cnidaria, Myxosporea) blood stages provides proteolytic arsenal as potential therapeutic targets against sphaerosporosis in common carp.BMC Genomics. 2020 Jun 16;21(1):404. doi: 10.1186/s12864-020-6705-y. BMC Genomics. 2020. PMID: 32546190 Free PMC article.
-
De Novo Assembly and Characterization of Four Anthozoan (Phylum Cnidaria) Transcriptomes.G3 (Bethesda). 2015 Sep 17;5(11):2441-52. doi: 10.1534/g3.115.020164. G3 (Bethesda). 2015. PMID: 26384772 Free PMC article.
-
De novo genome assembly of the Edwardsiid anthozoan Edwardsia elegans.G3 (Bethesda). 2025 Apr 17;15(4):jkaf011. doi: 10.1093/g3journal/jkaf011. G3 (Bethesda). 2025. PMID: 39849905 Free PMC article.
-
Sequencing and de novo transcriptome assembly of Anthopleura dowii Verrill (1869), from Mexico.Genom Data. 2016 Dec 5;11:92-94. doi: 10.1016/j.gdata.2016.11.022. eCollection 2017 Mar. Genom Data. 2016. PMID: 28066713 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

