Comprehensive analysis of β-catenin target genes in colorectal carcinoma cell lines with deregulated Wnt/β-catenin signaling
- PMID: 24467841
- PMCID: PMC3909937
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2164-15-74
Comprehensive analysis of β-catenin target genes in colorectal carcinoma cell lines with deregulated Wnt/β-catenin signaling
Abstract
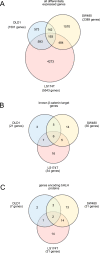
Background: Deregulation of Wnt/β-catenin signaling is a hallmark of the majority of sporadic forms of colorectal cancer and results in increased stability of the protein β-catenin. β-catenin is then shuttled into the nucleus where it activates the transcription of its target genes, including the proto-oncogenes MYC and CCND1 as well as the genes encoding the basic helix-loop-helix (bHLH) proteins ASCL2 and ITF-2B. To identify genes commonly regulated by β-catenin in colorectal cancer cell lines, we analyzed β-catenin target gene expression in two non-isogenic cell lines, DLD1 and SW480, using DNA microarrays and compared these genes to β-catenin target genes published in the PubMed database and DNA microarray data presented in the Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) database.
Results: Treatment of DLD1 and SW480 cells with β-catenin siRNA resulted in differential expression of 1501 and 2389 genes, respectively. 335 of these genes were regulated in the same direction in both cell lines. Comparison of these data with published β-catenin target genes for the colon carcinoma cell line LS174T revealed 193 genes that are regulated similarly in all three cell lines. The overlapping gene set includes confirmed β-catenin target genes like AXIN2, MYC, and ASCL2. We also identified 11 Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) pathways that are regulated similarly in DLD1 and SW480 cells and one pathway - the steroid biosynthesis pathway - was regulated in all three cell lines.
Conclusions: Based on the large number of potential β-catenin target genes found to be similarly regulated in DLD1, SW480 and LS174T cells as well as the large overlap with confirmed β-catenin target genes, we conclude that DLD1 and SW480 colon carcinoma cell lines are suitable model systems to study Wnt/β-catenin signaling and associated colorectal carcinogenesis. Furthermore, the confirmed and the newly identified potential β-catenin target genes are useful starting points for further studies.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Determinants of Wnt/β-catenin pathway dependency in colorectal cancer.Cell Cycle. 2012 Jan 1;11(1):9-10. doi: 10.4161/cc.11.1.18728. Epub 2012 Jan 1. Cell Cycle. 2012. PMID: 22157091 No abstract available.
-
Nuclear AXIN2 represses MYC gene expression.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2014 Jan 3;443(1):217-22. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2013.11.089. Epub 2013 Dec 2. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2014. PMID: 24299953 Free PMC article.
-
[Periplocin extracted from cortex periplocae induces apoptosis of SW480 cells through inhibiting the Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway].Ai Zheng. 2009 May;28(5):456-60. Ai Zheng. 2009. PMID: 19624870 Chinese.
-
Vitamin D and Wnt/beta-catenin pathway in colon cancer: role and regulation of DICKKOPF genes.Anticancer Res. 2008 Sep-Oct;28(5A):2613-23. Anticancer Res. 2008. PMID: 19035286 Review.
-
Transcriptional Regulation of Wnt/β-Catenin Pathway in Colorectal Cancer.Cells. 2020 Sep 19;9(9):2125. doi: 10.3390/cells9092125. Cells. 2020. PMID: 32961708 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Noncanonical activation of β-catenin by Porphyromonas gingivalis.Infect Immun. 2015 Aug;83(8):3195-203. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00302-15. Epub 2015 Jun 1. Infect Immun. 2015. PMID: 26034209 Free PMC article.
-
Tumor suppressor NDRG2 inhibits glycolysis and glutaminolysis in colorectal cancer cells by repressing c-Myc expression.Oncotarget. 2015 Sep 22;6(28):26161-76. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.4544. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 26317652 Free PMC article.
-
β-Catenin Knockdown Affects Mitochondrial Biogenesis and Lipid Metabolism in Breast Cancer Cells.Front Physiol. 2017 Jul 27;8:544. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2017.00544. eCollection 2017. Front Physiol. 2017. PMID: 28798698 Free PMC article.
-
Wnt/β-Catenin Target Genes in Colon Cancer Metastasis: The Special Case of L1CAM.Cancers (Basel). 2020 Nov 19;12(11):3444. doi: 10.3390/cancers12113444. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33228199 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MIBI-TOF: A multiplexed imaging platform relates cellular phenotypes and tissue structure.Sci Adv. 2019 Oct 9;5(10):eaax5851. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.aax5851. eCollection 2019 Oct. Sci Adv. 2019. PMID: 31633026 Free PMC article.
References
-
- He TC, Sparks AB, Rago C, Hermeking H, Zawel L, da Costa LT, Morin PJ, Vogelstein B, Kinzler KW. Identification of c-MYC as a target of the APC pathway. Science. 1998;15:1509–1512. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

