Determination of antibiotic consumption index for animal originated foods produced in animal husbandry in Iran, 2010
- PMID: 24468281
- PMCID: PMC3937136
- DOI: 10.1186/2052-336X-12-42
Determination of antibiotic consumption index for animal originated foods produced in animal husbandry in Iran, 2010
Abstract
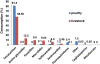
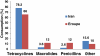
The public health concerns over the long-term exposure to antibiotics have risen in different parts of the world. The purpose of this study was to investigate the antibiotic consumption pattern in livestock and poultry and to estimate the quantity of antibiotic active ingredient (mg) consumed per unit weight (Kg) of red meat, milk and egg production in Iran in 2010. A cross-sectional study was designed in charmahal - bakhtiary province-Iran. A questioner has been developed by naming 110 types of antibiotics. Twenty two veterinary clinicians and three livestock pharmaceutical distributor companies were included in the survey to determine the antibiotic prescription and distribution pattern in the farms. Veterinary organization of Iran supplied the information of the total antibiotic consumption in different dosage forms. National and international data on the livestock and poultry production were obtained from the relevant official web sites. Tetracycline class of antibiotics was the most common types of antibacterial prescribed and sold to both livestock and poultry farms. Amino glycoside, penicillin and macrolide in the cattle farms and furofenocole in broiler farms were the second most used groups of antibiotics. The quantity of antibiotic active ingredients consumed per unit weight of animal-originated food products was counted as 107.4 mg/kg for both milk and red meat and 249.5 mg/kg for broiler meat and egg. Totally, it was estimated that 133 mg antibiotic substances was used per kg of milk, meat and egg produced in 2010. In comparison to available data for other countries, consumption of antibiotics in livestock and poultry in Iran is higher than developed countries with an exception of South Korea. The findings of the present study could be alarming for the legislative authorities in food security and safety. More clear evaluation should be carried out as well as implementation of national monitoring and inspective programs in order to reach an added safety regarding animal-originated foods.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Monitoring of antibiotic consumption in livestock: a German feasibility study.Prev Vet Med. 2012 Apr 1;104(1-2):34-43. doi: 10.1016/j.prevetmed.2011.10.013. Epub 2011 Nov 23. Prev Vet Med. 2012. PMID: 22115924
-
[Economic importance of antibiotic sale for private food animal practices in Switzerland - example veal production].Schweiz Arch Tierheilkd. 2020 Jul;162(7):471-480. doi: 10.17236/sat00268. Schweiz Arch Tierheilkd. 2020. PMID: 32618570 German.
-
Systematic analysis of occurrence, density and ecological risks of 45 veterinary antibiotics: Focused on family livestock farms in Erhai Lake basin, Yunnan, China.Environ Pollut. 2020 Dec;267:115539. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2020.115539. Epub 2020 Aug 29. Environ Pollut. 2020. PMID: 32892021 Free PMC article.
-
Chemistry, Antimicrobial Mechanisms, and Antibiotic Activities of Cinnamaldehyde against Pathogenic Bacteria in Animal Feeds and Human Foods.J Agric Food Chem. 2017 Dec 6;65(48):10406-10423. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.7b04344. Epub 2017 Nov 20. J Agric Food Chem. 2017. PMID: 29155570 Review.
-
Biodiversity conservation: The key is reducing meat consumption.Sci Total Environ. 2015 Dec 1;536:419-431. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.07.022. Epub 2015 Jul 29. Sci Total Environ. 2015. PMID: 26231772 Review.
Cited by
-
Bacterial community structures and biodegradation kinetic of Tiamulin antibiotic degrading enriched consortia from swine wastewater.J Environ Health Sci Eng. 2019 Dec 21;17(2):1121-1130. doi: 10.1007/s40201-019-00426-2. eCollection 2019 Dec. J Environ Health Sci Eng. 2019. PMID: 32030179 Free PMC article.
-
Dietary exposure to tetracycline residues through milk consumption in Iran.J Environ Health Sci Eng. 2015 Nov 23;13:80. doi: 10.1186/s40201-015-0235-6. eCollection 2015. J Environ Health Sci Eng. 2015. PMID: 26600942 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment of oxytetracycline and tetracycline antibiotics in manure samples in different cities of Khuzestan Province, Iran.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2015 Nov;22(22):17948-54. doi: 10.1007/s11356-015-5002-9. Epub 2015 Jul 14. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2015. PMID: 26165993
-
Antimicrobial Susceptibility Patterns and Genetic Diversity of Campylobacter spp. Isolates from Patients with Diarrhea in South Korea.Microorganisms. 2024 Jan 2;12(1):94. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms12010094. Microorganisms. 2024. PMID: 38257921 Free PMC article.
-
Occurrence and distribution of antibiotic resistance genes in water supply reservoirs in Jingjinji area, China.Ecotoxicology. 2017 Nov;26(9):1284-1292. doi: 10.1007/s10646-017-1853-9. Epub 2017 Sep 12. Ecotoxicology. 2017. PMID: 28900741
References
-
- World Health Organization (WHO) Use of antimicrobials outside human medicine and resultant antimicrobial resistance in humans. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2002.
-
- Nisha AR. Antibiotic residues - a global health hazard. Vet World. 2012;1:375–377.
-
- Botsoglou NA, Fletuvris DJ. Drug residue in food: pharmacology, food safety, and analysis. Chapter 3. New York: Basel: Marcel Dekker, Inc; 2001. p. 112.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources