Toxicity of phthalate esters exposure to carp (Cyprinus carpio) and antioxidant response by biomarker
- PMID: 24468924
- PMCID: PMC4012160
- DOI: 10.1007/s10646-014-1194-x
Toxicity of phthalate esters exposure to carp (Cyprinus carpio) and antioxidant response by biomarker
Abstract
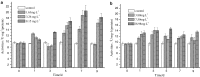
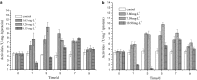
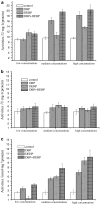
To study the toxic effects of phthalate esters on the aquatic creatures, carps were exposed to dibutyl phthalate (DBP) and di-2-ethylhexyl phthalate (DEHP) of six different concentrations for 96 h-LC50 measurements. It shows that the 96 h-LC50 is 16.30 and 37.95 mg L(-1), thus the safe concentration (1/10LC(50)) is 1.63 mg L(-1). The activities of xanthine oxidase (XOD) and catalase (CAT) were measured in liver to carp exposure for single or combinations of DBP and DEHP. The quantity of malonic dialdehyde (MDA) was also measured in the same way. XOD, CAT and MDA had shown an evident change while exposure time and concentration increased, combined exposure can aggravate this change. They might be used as early warning indicators and monitors, and have potentials in the ecological risk assessment.
Figures
References
-
- Biedermann-Brem S, Biedermann M, Pfenninger S, Bauer M, Altkofer W, Rieger K, Hauri U, Droz C, Grob K. Plasticizers in PVC toys and childcare products: what succeeds the phthalates? market survey 2007. Chromatographia. 2008;68:227–234. doi: 10.1365/s10337-008-0672-9. - DOI
-
- Bove JL, Dalven P. Pyrolysis of phthalic acid esters: their fate. Total Environ. 1984;36:313–318. doi: 10.1016/0048-9697(84)90282-1. - DOI
-
- Dizdaroglu M. Introduction to serial reviews on oxidative DNA damage and repair. Free Radic Bio Med. 2002;32:677. doi: 10.1016/S0891-5849(02)00766-9. - DOI
-
- Fang Y, Li W. Free radical and enzyme application in biology and medicine. Beijing: Science Press; 1989. pp. 42–371.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous