Generation of folliculogenic human epithelial stem cells from induced pluripotent stem cells
- PMID: 24468981
- PMCID: PMC4049184
- DOI: 10.1038/ncomms4071
Generation of folliculogenic human epithelial stem cells from induced pluripotent stem cells
Abstract
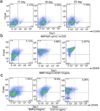
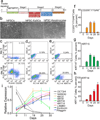
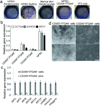
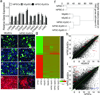
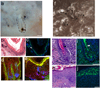
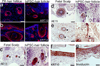
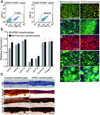
Epithelial stem cells (EpSCs) in the hair follicle bulge are required for hair follicle growth and cycling. The isolation and propagation of human EpSCs for tissue engineering purposes remains a challenge. Here we develop a strategy to differentiate human iPSCs (hiPSCs) into CD200(+)/ITGA6(+) EpSCs that can reconstitute the epithelial components of the hair follicle and interfollicular epidermis. The hiPSC-derived CD200(+)/ITGA6(+) cells show a similar gene expression signature as EpSCs directly isolated from human hair follicles. Human iPSC-derived CD200(+)/ITGA6(+) cells are capable of generating all hair follicle lineages including the hair shaft, and the inner and outer root sheaths in skin reconstitution assays. The regenerated hair follicles possess a KRT15(+) stem cell population and produce hair shafts expressing hair-specific keratins. These results suggest an approach for generating large numbers of human EpSCs for tissue engineering and new treatments for hair loss, wound healing and other degenerative skin disorders.
Figures
References
-
- Morris RJ, et al. Capturing and profiling adult hair follicle stem cells. Nat Biotechnol. 2004;22:411–417. - PubMed
-
- Ito M, et al. Wnt-dependent de novo hair follicle regeneration in adult mouse skin after wounding. Nature. 2007;447:316–320. - PubMed
-
- Cotsarelis G, Sun TT, Lavker RM. Label-retaining cells reside in the bulge area of pilosebaceous unit: implications for follicular stem cells, hair cycle, and skin carcinogenesis. Cell. 1990;61:1329–1337. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

